Thesis
The development of frontier AI models is increasingly capital-intensive. Training competitive large language models now requires sustained access to hundreds of thousands of advanced GPUs, dedicated networking infrastructure, large-scale data pipelines, and elite research talent. Each successive generation of models incurs higher costs, both in training and inference, as models grow larger. As model developers seek to develop new features in the hyper-competitive race to improve models, this cost curve is reshaping the structure of the AI industry. When models converge in quality, competitive advantages increasingly stem from model reliability, distribution, and the ability to withstand a race to the bottom in cost structure.
As development costs rise, pure play model developers face a structural challenge. Companies that rely solely on API revenue or consumer subscriptions must either reach massive scale quickly or access public markets to sustain continued model development against the spending spree spearheaded by the hyperscaler AI labs Google, Meta, Amazon, and Microsoft. Though “startup” labs like OpenAI, Anthropic, and xAI have raised unprecedented amounts of private capital, model economics increasingly resemble those of infrastructure companies rather than software startups. As venture funding slows and AI hype begins to dry in favor of an AI bubble, private labs are eyeing IPOs as a way to access fresh capital.
Against this background, vertically integrated AI companies hold a structural advantage. A vertically integrated model developer controls multiple layers of the AI stack, including data sources, distribution, hardware strategy, and end-user products. This structure subsidizes upfront model development costs, reduces customer acquisition costs, and reduces dependence on platforms controlled by the hyperscalers.
Elon Musk has followed the vertical integration playbook repeatedly across his multiple companies, including Tesla, SpaceX, and Neuralink, where capital-intensive core technologies are developed not as stand-alone products, but as connected ecosystems within the wider “Muskonomy.” Rather than operating as a standalone model provider, xAI is positioned as part of a broader ecosystem that includes X, Tesla, SpaceX, and other Musk ventures. The development of xAI’s own supercomputer cluster in Colossus and the March 2025 acquisition of X by xAI formalized this strategy by bringing a global consumer social media platform and a continuous stream of real-time data directly under xAI’s control to further the company’s vertical integration strategy.
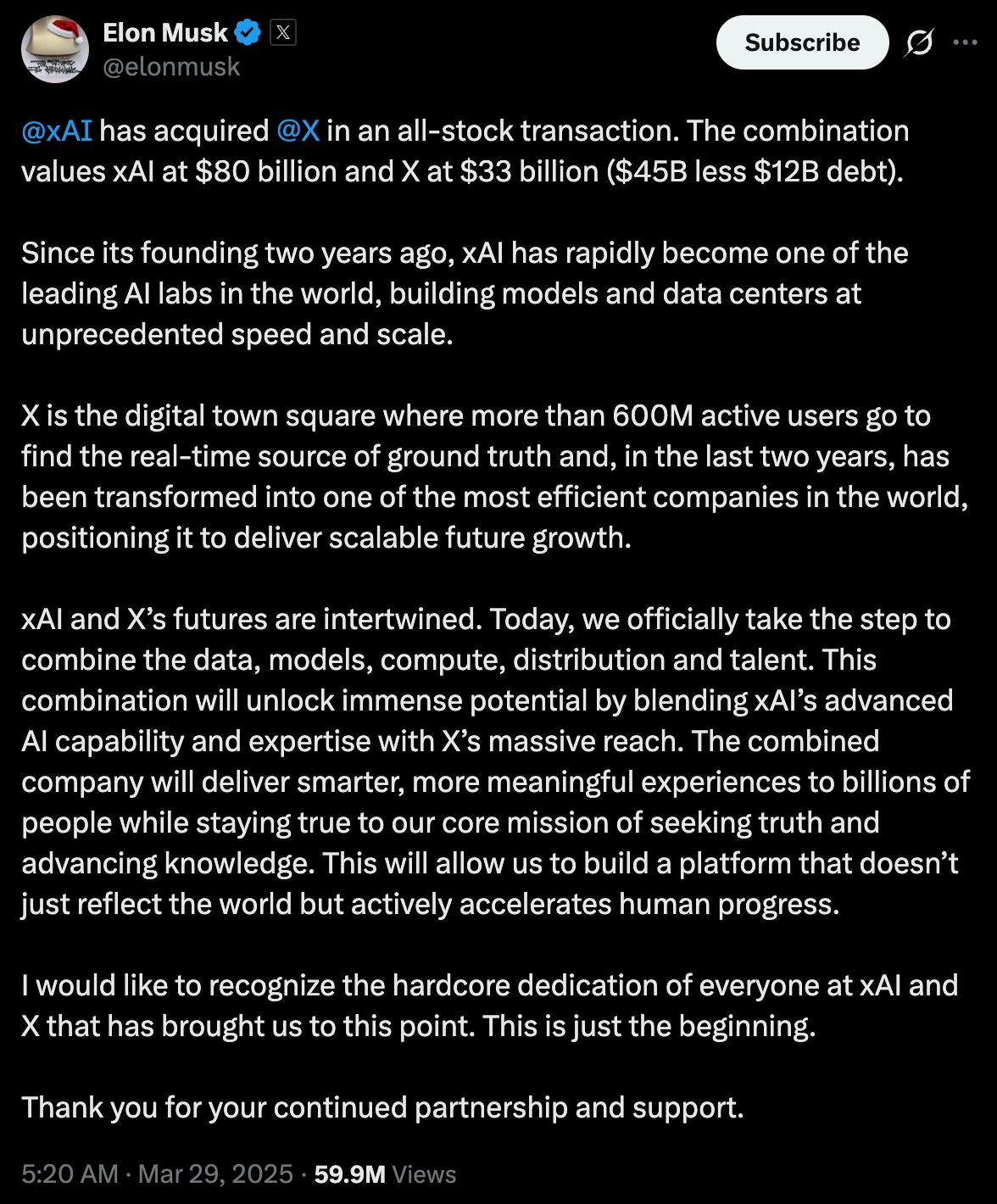
Source: Elon Musk
xAI’s long-term competitiveness depends less on any single benchmark win and more on whether its vertically integrated structure can sustainably finance frontier model development. If successful, xAI may avoid near-term pressure to pursue an IPO (and subsequent public scrutiny) by leveraging platform distribution and Musk-aligned capital to win the long-term AI future.
Founding Story
xAI was founded by Elon Musk in July 2023. Musk, known for his roles as CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, co-founder of Neuralink, the Boring Company, OpenAI, and his acquisition of Twitter (now X), established xAI with the ambitious goal to “understand the true nature of the universe.”
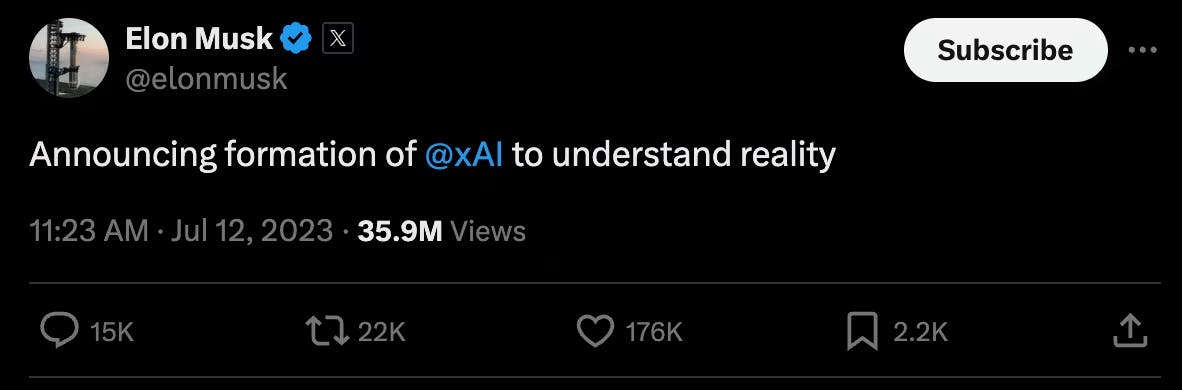
Source: X
Though Elon Musk founded xAI in 2023, the company’s origin predates the 2022 ChatGPT moment and dates back over a decade to a single conversation. In 2012, Musk met with Demis Hassabis, the co-founder of DeepMind, who warned him that artificial intelligence could become an existential threat if left unchecked. Taking the warning seriously, Musk invested in DeepMind shortly thereafter.
Source: LessWrong
Those concerns further intensified after Musk discussed DeepMind with Larry Page. Musk repeatedly raised the issue of AI safety in private conversations with Page, arguing that superintelligent systems could displace or endanger humanity if they were developed without sufficient alignment and control. Things came to a head at Musk’s 2013 birthday party:
“[Musk and Page] got into a passionate debate. Unless we built in safeguards, Musk argued, artificial-intelligence-systems might replace humans, making our species irrelevant or even extinct. Page pushed back. Why would it matter, he asked, if machines someday surpassed humans in intelligence, even consciousness? It would simply be the next stage of evolution. Human consciousness, Musk retorted, was a precious flicker of light in the universe, and we should not let it be extinguished. Page considered that sentimental nonsense. If consciousness could be replicated in a machine, why would that not be just as valuable? He accused Musk of being a “specist,” someone who was biased in favor of their own species. “Well, yes, I am pro-human,” Musk responded. “I f-cking like humanity, dude.”
When Google announced its acquisition of DeepMind in January 2014, Musk attempted to prevent the deal, telling Hassabis that the future of AI should not be controlled by a single corporation. When Hassabis continued with DeepMind’s acquisition anyway, and after Google’s internal “AI safety council” held just one meeting, Musk became convinced that existing institutions could not self-regulate AI development in the way he believed was necessary.
This led directly to the founding of OpenAI in December 2015. Musk co-founded OpenAI alongside Sam Altman as a nonprofit research organization. The stated goal was to create an open source, safety-oriented counterweight to Google and other large technology companies seeking to dominate AI development. Musk believed that distributing AI capabilities widely would reduce the risk of any single system becoming dominant or misaligned. He also believed that transparency would improve safety by allowing independent researchers to audit and challenge model behavior.
The relationship had begun to fracture by 2017. Musk grew frustrated with OpenAI’s pace and was increasingly concerned that it was falling behind Google. He proposed folding OpenAI into Tesla, arguing that Tesla’s compute infrastructure, real-world data, and capital base would provide a stronger foundation for safe AGI development. When other members of the OpenAI leadership rejected the proposal, Musk resigned from OpenAI’s board in 2018 and withdrew a significant portion of his planned funding. OpenAI subsequently created a capped profit structure and began raising large amounts of capital, with Microsoft investing as OpenAI’s first major corporate partner.
From Musk’s perspective, this transition represented a betrayal of OpenAI’s founding principles. He viewed the shift toward closed models and exclusive cloud partnerships as evidence that market incentives had overridden safety concerns. Simultaneously, the personal relationship between Musk and Altman deteriorated alongside the institutional one. By 2023, Musk was openly criticizing OpenAI and accusing it of becoming a de facto subsidiary of Microsoft rather than an independent steward of safe AI.
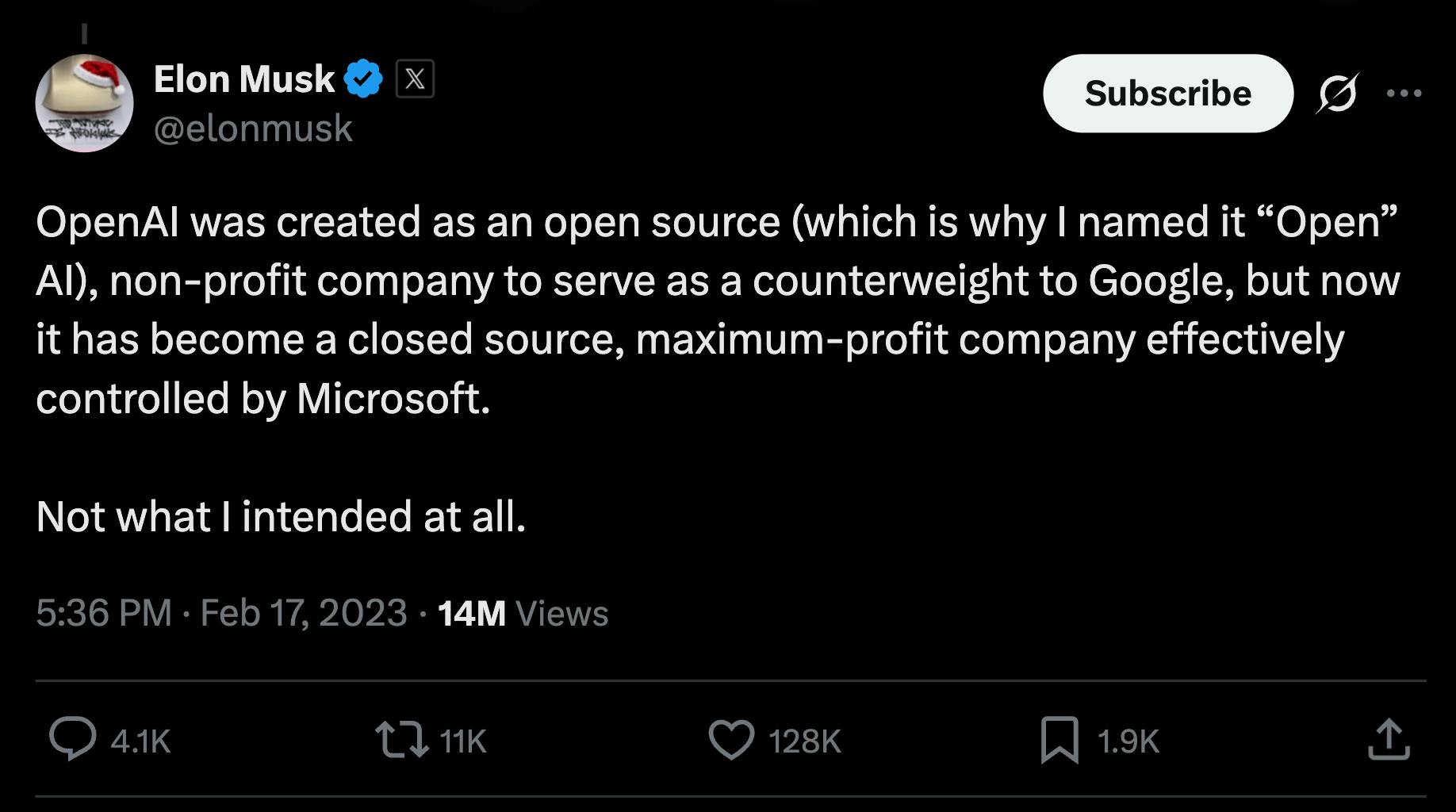
Source: Elon Musk
xAI was founded as a response to existing AI models as a challenger company emphasizing transparency, safety, and alignment with human values. xAI has said its mission is to build an AI that is “maximally truth-seeking” and focused on understanding the universe at a fundamental level. Designed to sit at the center of Musk’s broader company ecosystem, Musk has positioned xAI as the keystone to build applications combining the worlds of bits and atoms.
Founded with a deep bench of talent from leading AI research organizations, xAI was assembled to immediately compete at the frontier. Musk personally oversaw early hiring to recruit mission-aligned technical staff from competing AI labs and academic institutions.
Early technical leadership included Igor Babuschkin, a former DeepMind and OpenAI researcher who served as a co-founder and senior research lead during the initial development of Grok before departing in July 2025 to found his own venture capital firm. Other early senior research contributors included Tony Wu, formerly of Google DeepMind, and Greg Yang, formerly of Microsoft Research.
On the corporate side, xAI hired Mike Liberatore as CFO in April 2025 following his tenure at Airbnb and Twitter X, before he departed in July 2025 to join OpenAI. Legal leadership also experienced turnover, including the departure of general counsel Robert Keele in October 2025 for drone manufacturer Skydio. In October 2025, Musk appointed Anthony Armstrong, former vice chairman of investment banking at Morgan Stanley and senior advisor to the President, as CFO of xAI. In March 2025, xAI acquired X in an all-stock transaction, bringing the platform under xAI’s ownership. Following the acquisition, Linda Yaccarino resigned as CEO of X in July 2025.
Product
Grok
Grok is xAI’s flagship large language model, envisioned as a witty, “rebellious” AI assistant with real-time knowledge from X. First launched in November 2023, Grok has undergone rapid iterations to boost its reasoning, speed, and features. Below is a list of Grok’s core features, a timeline of Grok model releases, and model improvements over time:
As of January 2026, Grok’s core features include the following:
Document Analysis and Context: Grok supports summarizing and extracting key points from long documents for both consumers and developers, with workflows that emphasize condensing material into actionable findings. On the consumer side, xAI markets Grok as able to summarize, understand, and act on provided documents.
Agentic Coding: Grok functions as a code generation and explanation assistant for common languages and tasks, and xAI specifically frames Grok Code Fast 1 as an agentic model for writing code. In 2025, xAI expanded this capability into models and interfaces optimized for tool calling and coding workflows. Grok 4.1 Fast is a calling-focused model intended for real-world enterprise use cases, and xAI also ships separate reasoning and non-reasoning variants for developers to tune latency and depth.
Native Tool Use and Real-Time Search: Grok native tool use combined with real-time search integration. With Grok 4.1 Fast, xAI introduced an Agent Tools API that provides server-side access to capabilities such as real-time X data, web search, and code execution, with the model capable of deciding when to invoke tools during multi-step tasks and queries.
DeepSearch: Grok’s research mode is an agentic search workflow that can query both the web and X, follow links, and synthesize results rather than only generating a response from internal parameters. xAI’s describe the model as choosing its own search queries and “diving” as deeply as needed when answering difficult research questions, further emphasizing search within X using advanced keyword and semantic search tools.
Think Mode: Grok Think can be used for deeper reasoning-oriented queries, and xAI separately sells access to heavier variants through SuperGrok tiers, including SuperGrok Heavy. For developers, xAI’s 2025 releases repeatedly separated reasoning and non-reasoning variants so that “think longer” behavior can be applied selectively by product mode or API configuration.
Voice Mode / Voice Agent API: Grok Voice is offered across Grok’s apps, and xAI separately productizes the capability for developers via the Grok Voice Agent API. The Voice Agent API is positioned as supporting voice agents that can speak many languages, call tools, and search real-time data, and xAI describes it as built on the same stack that powers Grok Voice in mobile apps and Tesla vehicles. xAI also describes pricing for the Voice Agent API as a flat rate per minute of connection time.
Aurora Image Generation: Grok includes image generation capability in the consumer app as a built-in feature that turns text prompts into generated images.
Grok-1
The initial Grok model was reportedly built in just four months and debuted as an X-exclusive chatbot for paid users in November 2023. It was designed to answer questions with humor and fewer safeguards than its rivals, including “spicy” queries that other AI might refuse. Grok-1 already had real-time access to X’s data, giving it up-to-date knowledge of current events, which xAI touted as a unique advantage. Despite rapid development, xAI claimed that Grok was on par and even “surpassed” other models. However, the model’s unfiltered style also meant that Grok courted early controversies, where the model would share incorrect or potentially dangerous information.
Grok-1.5
xAI’s first major upgrade focused on boosting reasoning and context handling. Grok-1.5, released in March 2024, expanded the model’s context window to 128K tokens, allowing it to ingest and analyze extremely long documents (up to 128K tokens, 16x the previous limit). Its problem-solving skills improved significantly; for example, Grok-1.5 scored 50.6% on the MATH benchmark (versus 23.9% for Grok-1) and 90% on GSM8K, reflecting much better performance on math word problems. Coding abilities also jumped, with Grok-1.5 achieving 74.1% on HumanEval code generation (up from 63.2% in Grok-1).
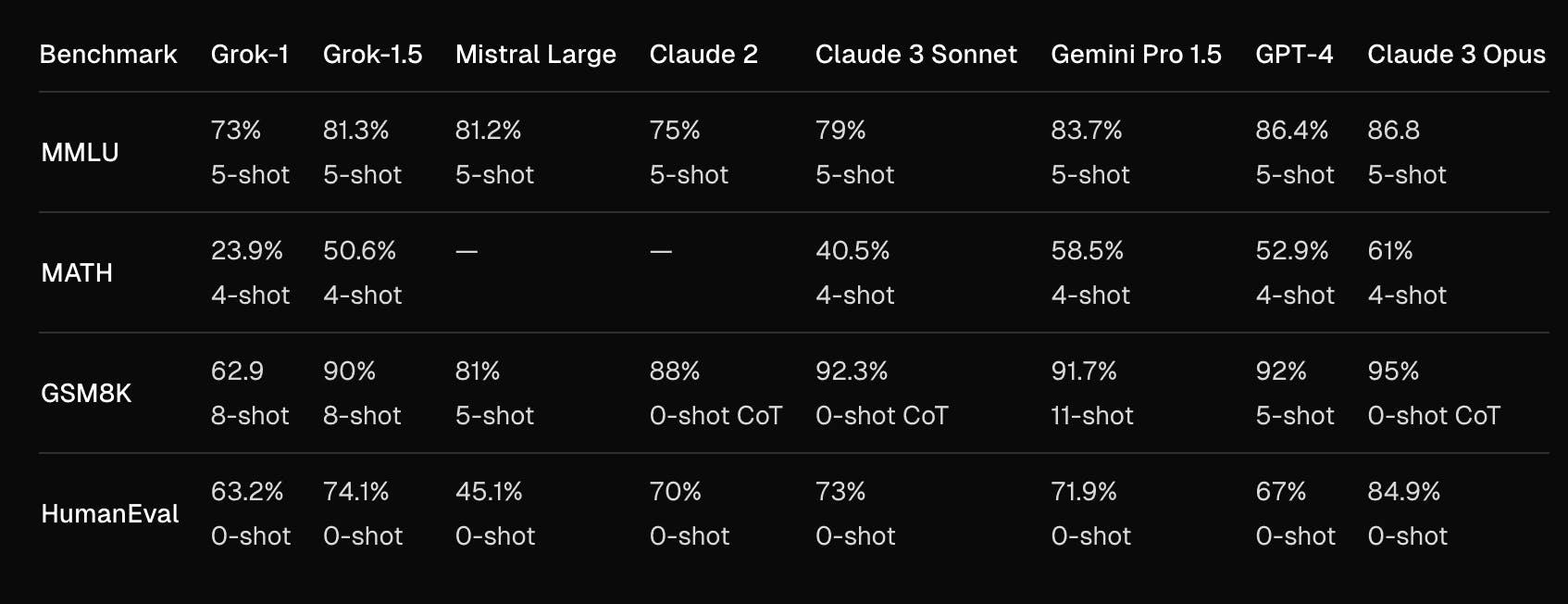
Source: xAI
These gains narrowed the gap with top models: for instance, Grok-1.5 reached 81.3% on the MMLU knowledge benchmark, approaching GPT-4’s approximately 86% on that test. Around this time, xAI also released Grok-1’s model weights publicly, signaling a company move towards AI transparency and inviting community feedback.
Grok-2 & Grok-2 Mini
Introduced in August 2024, Grok-2 brought “significant improvements” in reasoning, accuracy, and versatility over its predecessor. xAI noted that Grok-2 could identify missing information in a prompt and reason through event sequences more effectively. Internal tests showed it outperformed OpenAI’s GPT-4 and Anthropic’s Claude on some benchmarks. Grok-2 retained a high degree of instruction-following and added multilingual support, answering in multiple languages with greater accuracy. Upon launch, the full Grok-2 model was accessible only to X Premium subscribers (for $8 per month).
Source: xAI
Alongside the full model, xAI released a distilled Grok-2 Mini, a smaller LLM optimized for speed and cost-efficiency. The Mini model was offered as an option in X’s interface, letting users trade off output richness for faster responses. By the end of August, xAI also made Grok-2 (and Mini) available via its enterprise API, giving developers a cheaper, more efficient model choice for integration.
Bringing Grok to Everyone
In December 2024, an upgraded Grok-2 model was rolled out platform-wide, with improved response speed, better accuracy, and multilingual understanding. Notably, Grok gained the ability to perform live web searches and cite sources in its answers. When asked about current news or factual queries, Grok could retrieve relevant posts from X or webpages on the internet and display them with inline citations, a move aimed at improving answer reliability and user trust for both X and Grok. xAI also integrated image generation into Grok at this time via the Aurora model, enabling users to ask Grok for pictures or memes.
xAI also opened Grok access to all X users for free (ad-supported), albeit with rate limits (for example, 10 queries every two hours). Paying subscribers on X (Premium and Premium+) received higher usage caps and early access to new capabilities. Additionally, a new “Grok button” began appearing on X posts, allowing users to click and have Grok analyze or explain a tweet in context.
Source: xAI
Grok 3 Beta & Grok 3 Mini
Unveiled as an early preview in February 2025, Grok 3 was trained on xAI’s owned compute cluster (Colossus), reportedly using “ten times” more compute than any prior state-of-the-art model. Grok 3 demonstrated markedly better performance than prior Grok models in reasoning, mathematics, coding, world knowledge, and following complex instructions.
According to xAI, Grok 3 exhibits “leading performance across both academic benchmarks and real-world user preferences,” attaining an Elo score of 1402 (and top half in placements) on the Chatbot Arena ranking. Grok 3 also exhibits top performances across standard AI benchmarks, including graduate-level science knowledge (GPQA), general knowledge (MMLU-Pro), and math competition problems (AIME).
Source: Chatbot Arena
As of February 2025, Grok 3 was being rolled out to X’s Premium/Premium+ users and the Grok web/app clients, with Premium+ subscribers receiving immediate access to the “Think” reasoning mode and a new “DeepSearch” feature. All users, including those on the free tier, are expected to receive access to Grok 3’s improved capabilities over time as xAI continues training and fine-tuning the model with user feedback during the beta.
Grok 4
In July 2025, xAI released Grok 4, positioning it as its most capable general-purpose model to date. Grok 4 was trained using large-scale reinforcement learning on xAI’s Colossus cluster, which comprises approximately 200K GPUs, and leveraged more than an order of magnitude more compute than previous Grok generations.
Grok 4 introduces native tool use, allowing the model to autonomously invoke code execution, web search, and X search during inference. On academic benchmarks, Grok 4 achieved state-of-the-art results among closed models, including 25.4% on Humanity’s Last Exam, 37.5% on USAMO 2025, and 90.0% on AIME’25. Grok 4 was made available to SuperGrok and X Premium+ subscribers, as well as through the xAI API.
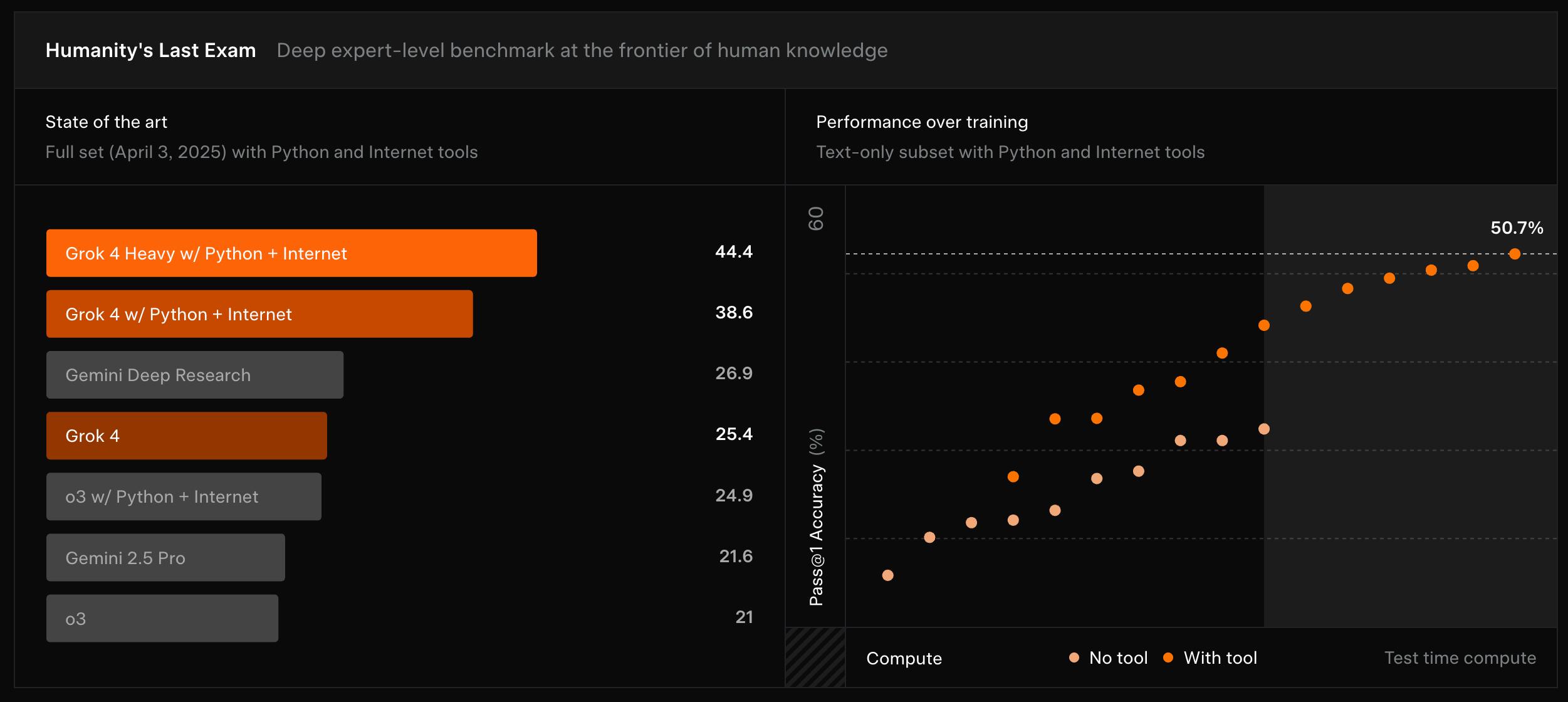
Source: xAI
Alongside the base model, xAI launched Grok 4 Heavy, a high test-time compute variant that runs multiple parallel reasoning traces. Grok 4 Heavy became the first model to score 50% on Humanity’s Last Exam (text-only subset) and led multiple competitive benchmarks, including 61.9% on USAMO’25 and 100% on AIME’25 with Python tools.
Source: xAI
Grok Code Fast 1
In August 2025, xAI introduced grok-code-fast-1, a purpose-built model optimized for agentic coding workflows. Training using a programming-heavy training corpus, grok-code-fast-1 emphasizes low latency, rapid tool invocation, and cost efficiency. xAI reported inference speeds of approximately 190 tokens per second, significantly faster than general-purpose frontier models. The model launched with integrations across developer platforms, including GitHub Copilot, Cursor, Cline, Windsurf, and others.
Grok 4 Fast
In September 2025, xAI released Grok 4 Fast, a cost-efficient general reasoning model derived from Grok 4. Grok 4 Fast was trained with large-scale reinforcement learning to maximize “intelligence density,” achieving comparable benchmark performance to Grok 4 while using 40% fewer thinking tokens on average. xAI reported that this translated into a 98% reduction in cost to reach equivalent benchmark performance.
Grok 4 Fast supports a 2-million token context window, native web and X search, and a unified architecture that handles reasoning and non-reasoning responses within a single model. On benchmarks, Grok 4 Fast scored 92.0% on AIME 2025, 93.3% on HMMT 2025, and 85.7% on GPQA Diamond (no tools). The model ranked first on LMArena’s Search Arena during private evaluation and was made available to all Grok users.
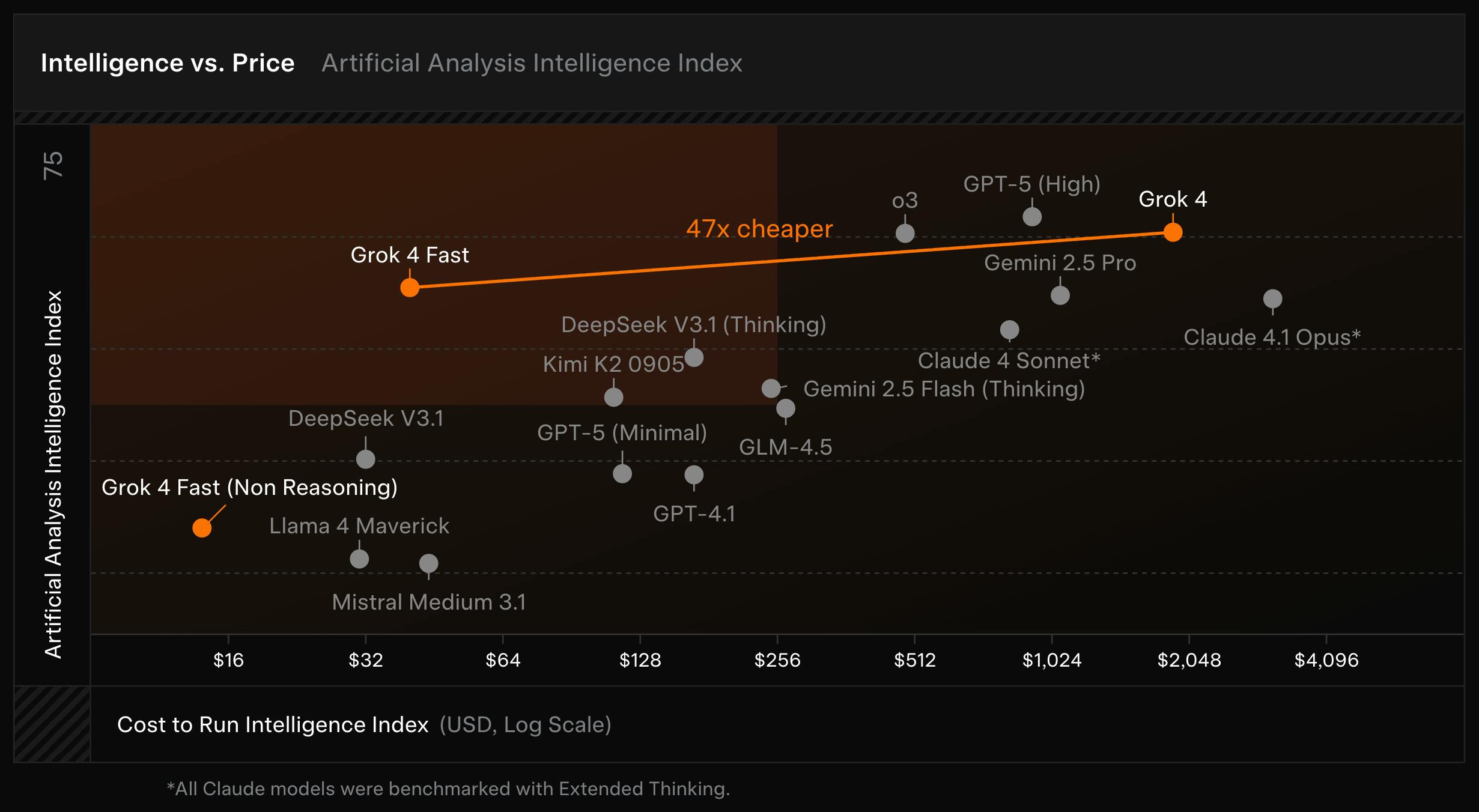
Source: xAI
Grok 4.1
In November 2025, xAI released Grok 4.1, a model focused on improving real-world usability, stylistic coherence, and emotional intelligence while retaining Grok 4’s reasoning performance. On LMArena’s Text Leaderboard, Grok 4.1 Thinking ranked first overall with 1483 Elo, while the non-reasoning variant ranked second at 1465 Elo, outperforming several competitors’ full reasoning configurations. Grok 4.1 also showed significant gains on interpersonal benchmarks, scoring 1586 Elo on EQ-Bench3, the highest reported result at the time.
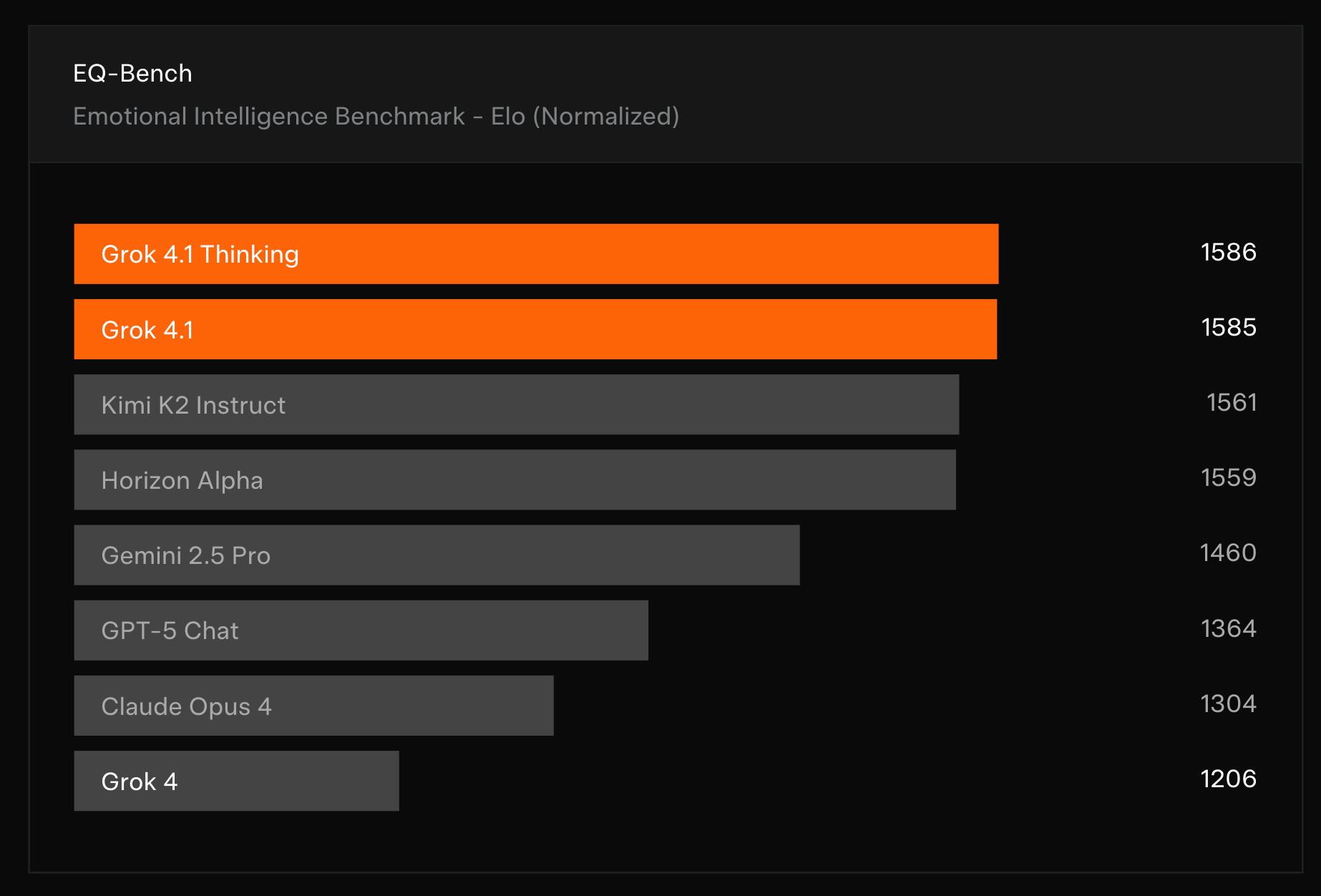
Source: xAI
Grok 4.1 Fast & Agent Tools API
Later in November 2025, xAI released Grok 4.1 Fast alongside the Agent Tools API. Grok 4.1 Fast was optimized specifically for long-horizon, tool-calling agent workflows and maintained a 2-million-token context window. On τ²-bench Telecom, an AI agent customer support benchmark, Grok 4.1 Fast achieved close to a 100% accuracy at a total cost of $105.
The accompanying Agent Tools API provides server-side access to web search, X search, code execution, file retrieval, and MCP-compatible external tools, enabling fully autonomous agents without developer-managed infrastructure. Pricing for Grok 4.1 Fast was set at $0.20 per million input tokens and $0.50 per million output tokens, with tool calls billed separately.
Grok Voice Agent API
In December 2025, xAI launched the Grok Voice Agent API, extending Grok’s capabilities into real-time voice interactions. The voice stack, including VAD, tokenization, and audio models, was trained entirely in-house. The API launched at a flat rate of $0.05 per minute of connection time, undercutting major voice AI providers. Grok Voice Agents support dozens of languages, dynamic code and search tool usage, and are integrated for use in Tesla vehicles.
Aurora
Aurora is xAI’s in-house text-to-image generative model, which powers Grok’s ability to create images. Released in December 2024, Aurora represents xAI’s answer to other leading image generation models. Aurora is an autoregressive mixture-of-experts model trained on interleaved text and image data. This means the model treats image generation as a sequence prediction problem. Given a text prompt (and optionally an input image), it generates the next “tokens” step-by-step, where each token represents a part of the image. Trained on billions of examples from the internet, Aurora has developed a broad understanding of how visual concepts correspond to language. Aurora allows users to convert text prompts into AI-generated images and multimedia outputs. Premium users benefit from enhanced creative capabilities, including the generation of artwork, logos, and prototype video clips. This expanded functionality supports a range of applications from graphic design to media production, delivering high-quality content with minimal user input.

Source: xAI
X Integration
Elon Musk has tightly integrated Grok into the X platform as both a distribution tool and a testing ground. xAI’s acquisition of X further bundled the social media platform into xAI permanently as a customer distribution platform and data source.
Initially, access to Grok was restricted to paid X subscribers, which limited the user base but also allowed xAI to iterate with a controlled group. Over the course of 2024, integration deepened as Grok became available via X’s mobile apps and website (through a chat interface at grok.com or an “Ask Grok” option on X). The introduction of the “Grok” button on tweets in late 2024 allowed users scrolling their feeds to ask Grok to contextualize or analyze a post (for example, summarizing a long thread, explaining a meme, or providing background on a news item).

Source: X
Grok’s ability to pull real-time data from X gives Grok an edge in addressing questions about ongoing events. The model leverages recent X posts as well as external web content to produce answers to queries about past and current events. When queried, Grok will search the platform and the web, then respond with answers that include linked citations to sources like recent news articles or viral posts.
xAI API
In November 2024, xAI launched a public beta of its developer API, allowing third parties to build applications on top of Grok and related models. xAI explicitly made its REST API compatible with existing SDKs so that migrating an app to use Grok from rival model developers OpenAI and Anthropic is as simple as swapping out the API endpoint URL. This compatibility lowers the barrier for developers who want to switch to using Grok as their AI backend.
Source: xAI
The API supports features like function calling, system messages for role instructions, and extended context processing for applications needing long documents. Developer feedback indicates Grok’s high steerability as a double-edged sword: great flexibility, but requiring developers to implement their own safety filters.
Source: xAI
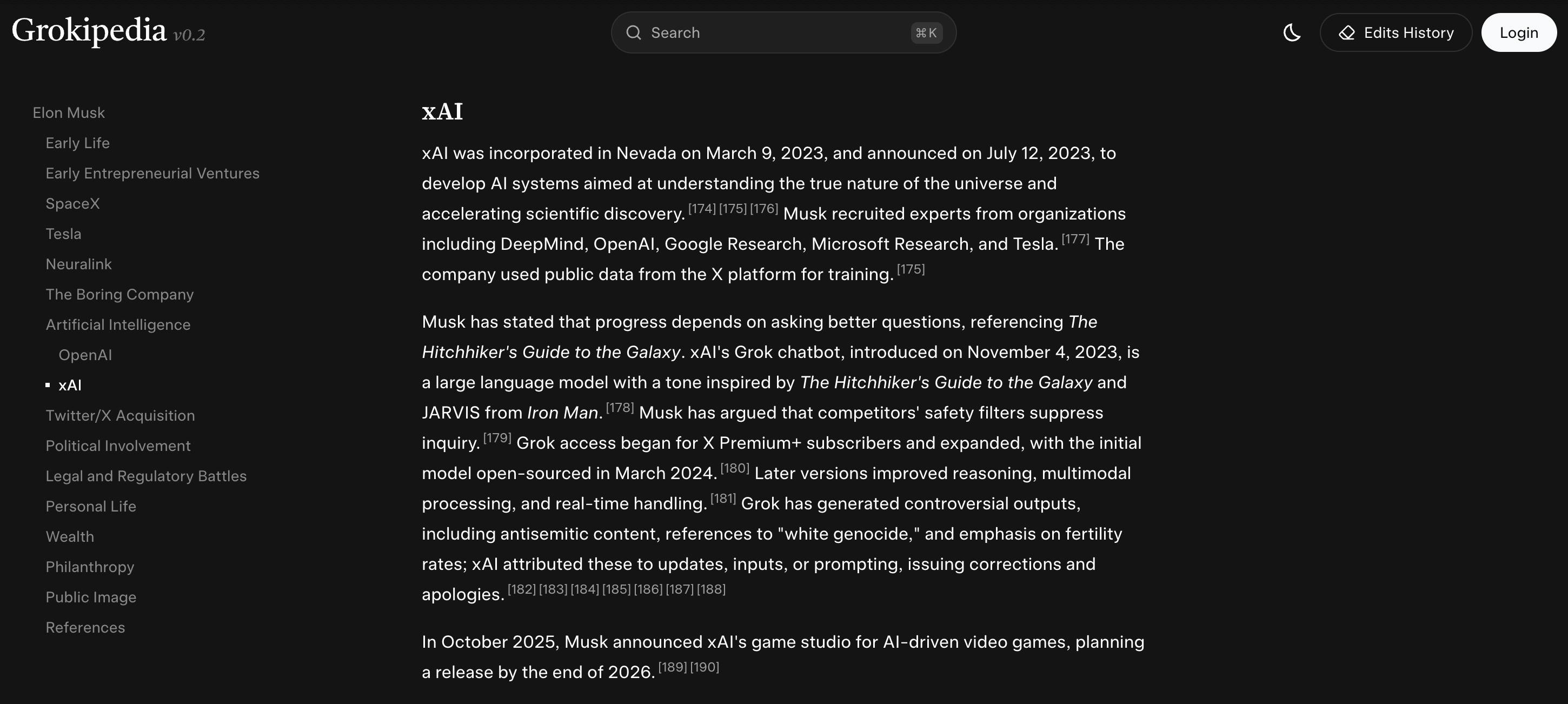
Grokipedia
Launched in October 2025, Grokipedia is xAI’s AI-generated online encyclopedia that aims to package Grok’s “world knowledge” into a Wikipedia-like reference product. Grokipedia would systematically update early versions of the product (labeled using vX.X format) shipped with a minimalist interface centered on search, and debuted with roughly 885K articles, an order of magnitude smaller than English Wikipedia’s 7 million pages, but large enough to function as a general-purpose lookup layer for Grok and X users. As of Januar 2026, the site has over 1 million articles.
At launch, Grokipedia pages resembled stripped-down Wikipedia entries with headings, subheadings, and citations, but did not appear to support open community editing in the way Wikipedia does. Reports noted that editing controls were limited and changes lacked clear attribution, with users generally unable to submit direct edits themselves. Grokipedia’s entries are largely generated (and “fact-checked”) by Grok, with a substantial portion forked or adapted from Wikipedia, in some cases copied nearly verbatim, with Wikipedia-derived pages carrying CC BY-SA 4.0 while most other entries fall under an “X Community License.”
Source: Grokipedia
Though Grokipedia has the end goal of eschewing all human bias, academic reports find that AI-driven editing can also be prone to political bias. In addition, Grokipedia pages are “substantially longer and contain significantly fewer references per word” when compared to Wikipedia, and entries often show divergent editing conventions, largely stemming from some pages being derived directly from Wikipedia versus others being Grok-edited.
Musk intends for Grokipedia to eventually be a modern-day “Library of Alexandria,” a permanent font of knowledge that is automatically updated as human understanding advances, hearkening back to xAI’s ultimate mission: “to understand the true nature of the universe.”
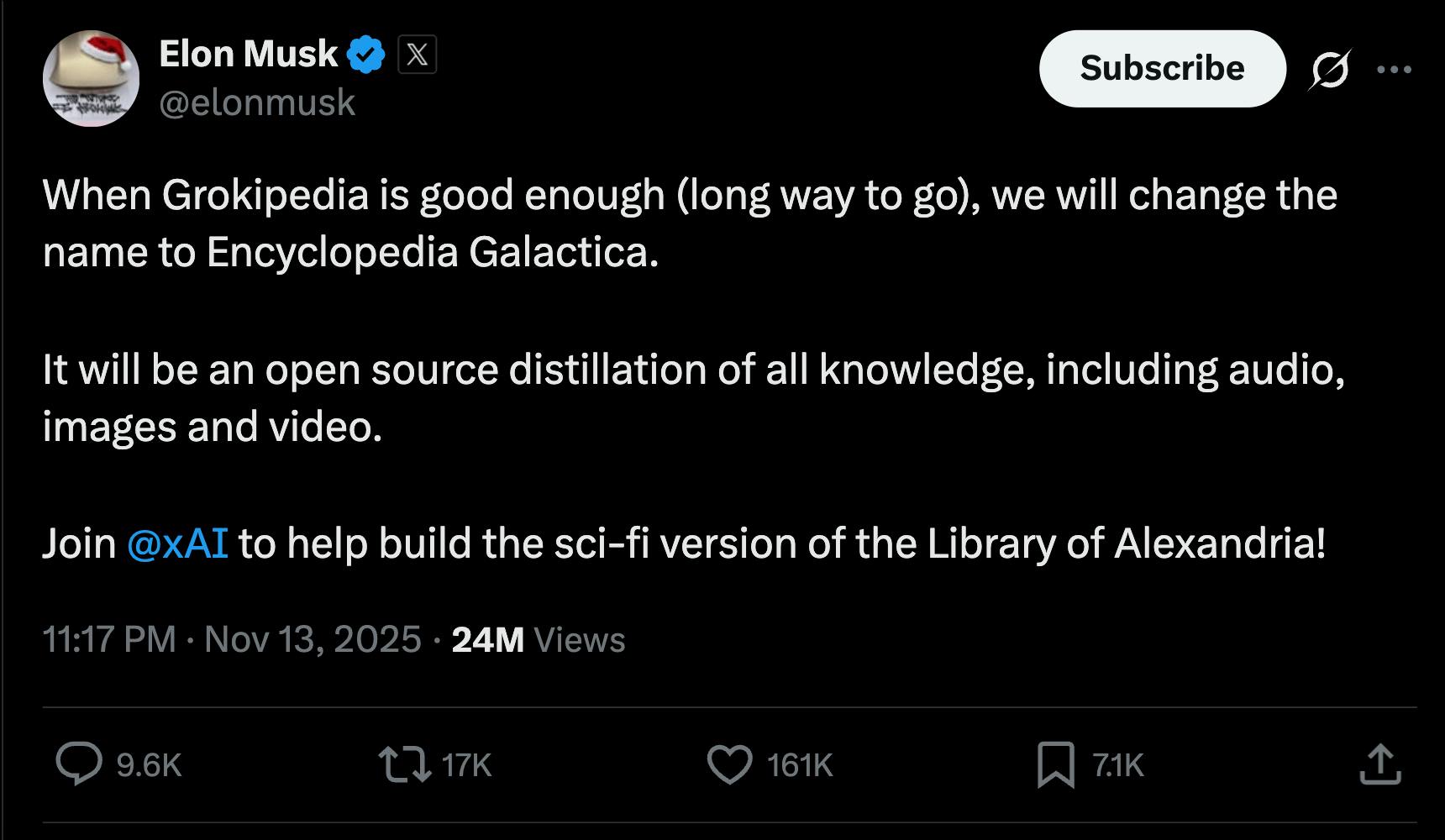
Source: Elon Musk
Colossus
Colossus is xAI’s high-powered computing cluster, purpose-built to train and run advanced AI models. xAI claims that Colossus is “the world’s biggest supercomputer.” The supercomputer was constructed by SuperMicro over 122 days in 2024. Jensen Huang, the CEO of Nvidia, explained how that compares to a typical supercomputer: “A supercomputer that you would build would take, normally, three years to plan, and then they deliver the equipment, and it takes one year to get it all working.” Elon Musk has claimed that Colossus is “the most powerful AI training system yet.” As of January 2026, Colossus has reached a scale of over 200K GPUs and retains an ultimate goal of 1 million GPUs.

Source: Supermicro
While the exact hardware details are not fully disclosed, Colossus currently consists of NVIDIA’s AI accelerators (H200 / H100 GPUs) connected via the NVIDIA Spectrum-X Ethernet networking platform. Colossus is engineered for previously unprecedented throughput: with 200K GPUs, the cluster has an aggregate memory bandwidth of approximately 194 petabytes per second and over one exabyte of storage capacity. Each server node is connected with 3.6 terabits per second of network bandwidth, designed to minimize bottlenecks and accelerate sizable distributed training.

Source: xAI
When compared with past AI supercomputing efforts, such as the Microsoft/OpenAI Azure supercomputer (10K GPUs), Meta’s Research SuperCluster (16K GPUs), or the Nvidia Eos (10.7K GPUs), Colossus stands out due to its sheer scale. Estimates suggest that at the full planned scale, Colossus (200K H100 GPUs) could theoretically deliver around 800 exaFLOPs of AI compute, significantly outperforming current publicly known systems. In comparison, El Capitan, which surpassed Frontier as the world’s most powerful traditional supercomputer in November 2024, aims to peak at two exaFLOPs, meaning Colossus at full scale would surpass its compute 400x.
Precise estimates of AI infrastructure among top industry players can be difficult to ascertain, as publicly reported data on exact GPU counts and allocations vary significantly and often lack transparency. However, analysis of ballpark estimates for computing resources available at major firms gives the following year-end 2024 estimates and 2025 projections:
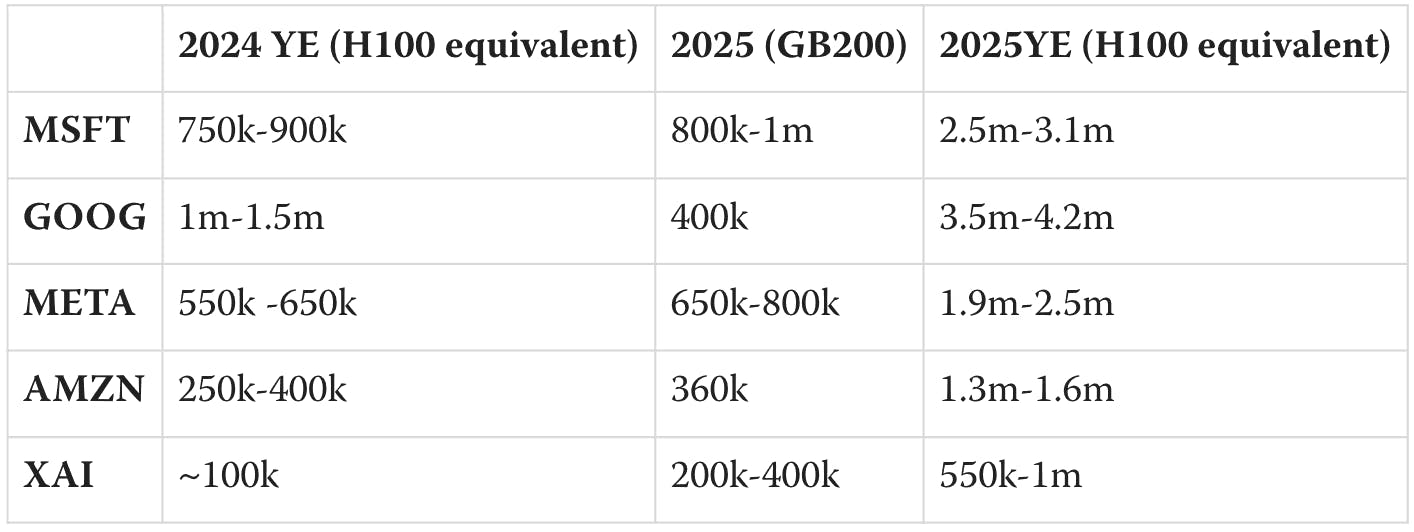
Source: LessWrong
Given estimates for past AI foundational model training, approximate compute differences between H100 and A100 GPUs, and scaling laws, one report notes that xAI’s AI infrastructure is positioned similarly to fellow foundational model startups:
“If xAI is able to devote a similar fraction of its compute to training as OpenAI or Anthropic… its training is likely to be similar in scale to Anthropic and somewhat below OpenAI and Google.”
Source: Epoch AI
Colossus is the backbone of xAI’s product suite, underpinning Grok’s models and future feature innovations. It enables compute-intensive approaches such as Grok’s “DeepSearch” mode, where extra GPU cycles are allocated per query for deeper reasoning. As xAI attempts to train even larger models (with multiple trillions of parameters), Colossus serves as the underlying infrastructure that makes such ambitions feasible. Moreover, Colossus provides xAI full control of its hardware, removing dependence on external cloud providers.
Strategically, xAI is positioning itself as a vertically integrated, full-stack AI powerhouse: from foundational models (Grok) to massive AI infrastructure (Colossus) to broad consumer (via X and Grok apps) and enterprise reach (Grok API).
Market
Customer
xAI’s Grok has applications across a wide array of industries, with use cases for both consumers and enterprises. xAI's immediate customer base comprises Grok users, X users, and Premium subscribers, representing the most engaged users of X's premium services. In addition, Elon Musk announced Grok would have a standalone consumer app in January 2025. As of January 2026, the app had reportedly been downloaded 60 million times.
Beyond its consumer-facing distribution through X integrations and the Grok app, xAI aims to capitalize on developer users. Its release of an enterprise API in October 2024 is designed to offer Grok as a standalone AI tool or embedded foundational model in software applications, especially for companies unable to develop an in-house alternative large AI model. Though technical specifications are in the early stages, xAI is comparable with competing labs such as OpenAI and Anthropic in ease of access and business intent.
In July 2025, xAI announced “xAI for Government,” a promise to provide a suite of government-specific AI products and a call-to-action to hire forward-deployed engineers to develop those products. xAI also revealed two milestones in government contracting, a $200 million ceiling contract with the US Department of Defense (also awarded to Anthropic, Google, and OpenAI) and xAI products available for purchase through the US General Services Administration.
Market Size
Generative AI is expected to significantly impact industries requiring significant human hours and knowledge work. Sectors such as healthcare, finance, legal services, and software development, where human knowledge workers have traditionally shouldered the bulk of high-value tasks, have seen the most value accrual in AI platforms.
Generative AI tools like xAI’s Grok, OpenAI’s GPT, or Anthropic’s Claude, designed to handle interdisciplinary tasks such as mathematical reasoning, coding, and real-time data processing, can significantly improve efficiency across these sectors. J.P. Morgan estimates that “half of the vulnerable jobs in the United States will be automated away over the next 20 years” with a total productivity gain of “about 17.5% or $7 trillion beyond the current Congressional Budget Office projection for GDP.”
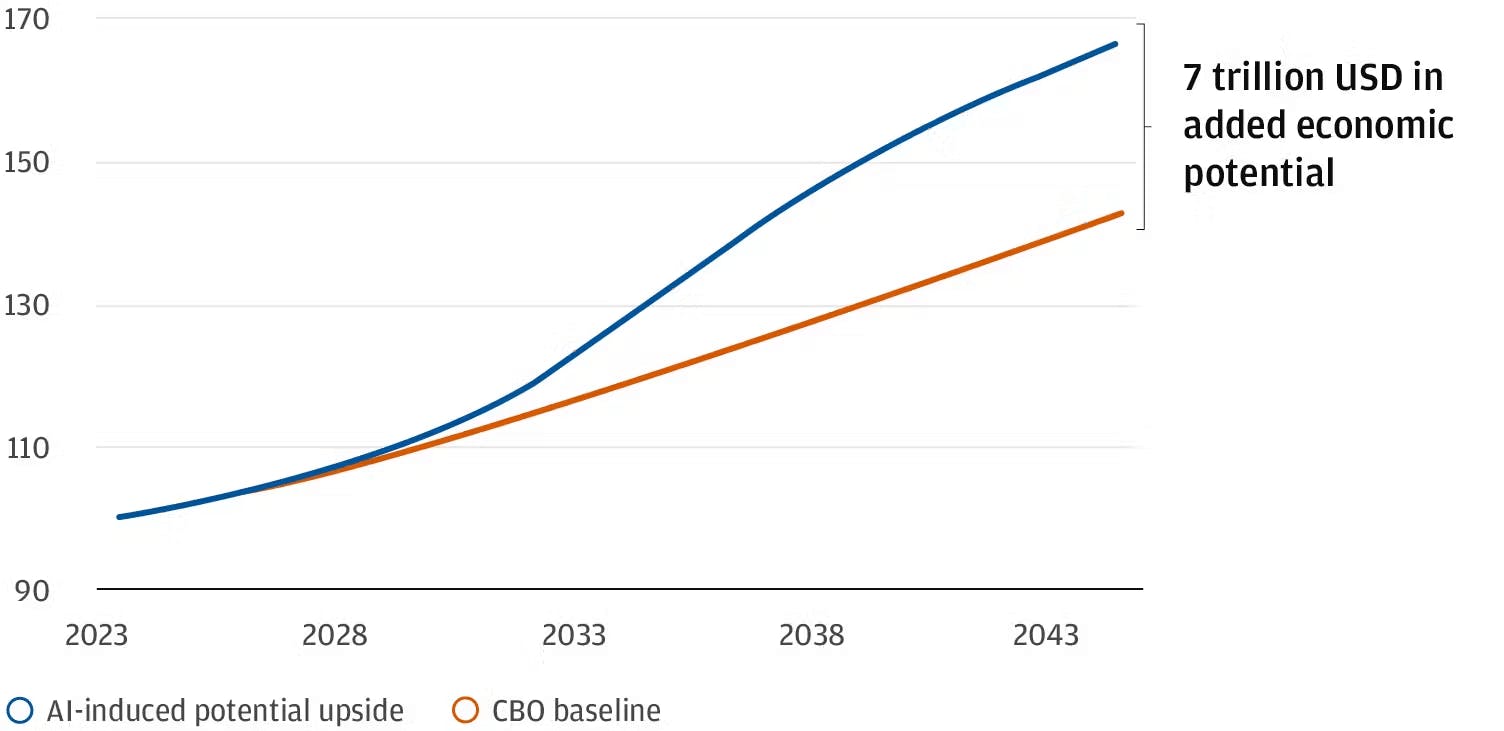
Source: J.P. Morgan
The generative AI market was valued by Bloomberg at $40 billion in 2023, and Bloomberg estimates a total market value of $1.3 trillion by 2032, growing at a 42% CAGR over the period. Other estimates are less bullish but still project a final market size of over $1 trillion by 2032. This rapid growth is mainly predicated on the adoption trends of AI technologies continuing to grow exponentially. According to Forbes in 2024, 97% of all business owners believe ChatGPT will help their business. Similarly, PwC estimated in 2023 that nearly 73% of all US companies have implemented generative AI in some area of business.
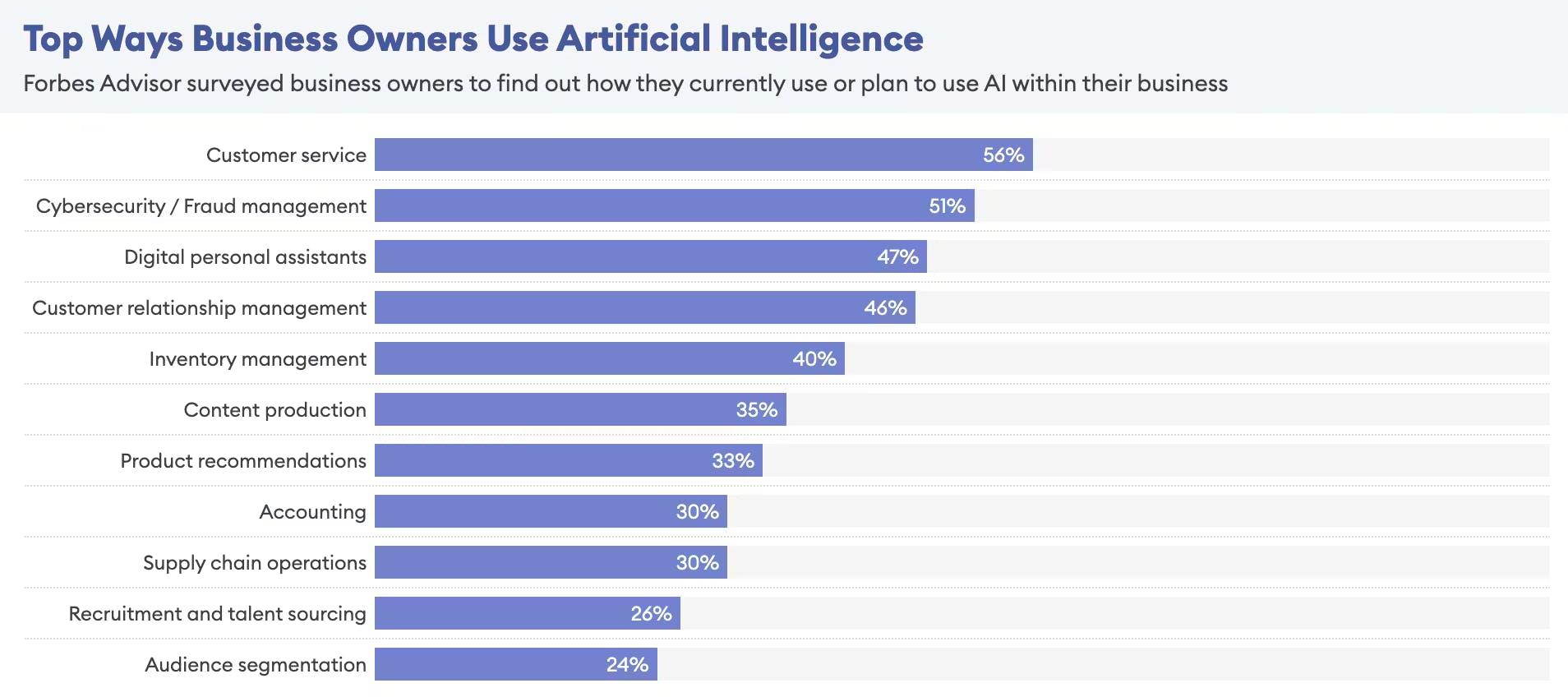
Source: Forbes
Competition
Though xAI has established itself as a notable player in artificial intelligence, it faces significant competition for dominance from existing AI frontrunners like OpenAI, Anthropic, Google DeepMind, and Meta AI Research, all vying for advancements in model development, enterprise adoption, and industry-defining innovations.
Startups
OpenAI: Founded in 2015 and based in San Francisco, OpenAI is a consumer and enterprise AI platform built around the GPT model family and the ChatGPT product. ChatGPT reached over 100 million monthly users within two months of launch and serves roughly 800 million weekly active users as of October 2025, including more than 1.5 million enterprise customers and over 10 million paying subscribers. In March 2025, OpenAI raised $40 billion at a $300 billion valuation led by SoftBank, followed by an additional $8.3 billion in August 2025, bringing total funding to $57.9 billion and making it the most well-funded AI company as of January 2026.
OpenAI operates a large-scale API business alongside ChatGPT while maintaining a deep infrastructure and commercialization partnership with Microsoft, and is one of the founding members of the US Stargate Project announced in January 2025. Despite formal safety teams and initiatives, OpenAI has faced sustained internal and external criticism over the prioritization of rapid product deployment over safety, highlighted by multiple high-profile departures of alignment and research leaders between 2024 and 2025. The company has reportedly considered an IPO in 2026.
Anthropic: Founded in 2021 and headquartered in San Francisco, Anthropic has raised $33.7 billion in total funding with a valuation of $183 billion as of January 2026. The company develops the Claude model family, which it advertises as having high reliability, long context reasoning, and enterprise deployment rather than consumer appeal. Founded by former OpenAI researchers, Anthropic emphasizes its primary focus on AI safety and alignment via its Constitutional AI framework. Anthropic operates primarily as an API first business with deep integration into enterprise and developer platforms, emphasizing regulated, safety-critical, and large-scale professional use cases over mass market consumer distribution. The company is reportedly considering an IPO by early 2026 and is in talks to secure further funding that could push Anthropic’s valuation to $350 billion.
Cohere: Founded in 2019 in Toronto, Canada, Cohere focuses on enterprise-grade language models designed for secure, controlled, and private deployment. As of 2025, Cohere’s platform centers on its latest Command series models optimized for retrieval augmented generation, multilingual reasoning, and regulated industry workloads, with deployment support across Oracle Cloud, Google Cloud, and AWS. In August 2025, Cohere raised $500 million at a $6.8 billion valuation, followed by an additional $100 million extension in September 2025. Oracle remains Cohere’s primary strategic partner, embedding Cohere models directly into Oracle Database, Fusion applications, and OCI Generative AI services, reinforcing Cohere’s positioning as an independent enterprise LLM provider rather than a consumer AI platform.
Mistral AI: Founded in 2023 and based in Paris, Mistral AI has positioned itself as Europe’s leading independent AI lab with a strong emphasis on open and efficient foundation models. In December 2025, the company released the Mistral 3 family of open-weight models (14B, 8B, and 3B dense models plus Mistral Large 3 with sparse MoE architecture), designed to run from edge devices to cloud and released under permissive licenses. In September 2025, Mistral closed a €1.7 billion ($2 billion) Series C funding round led by semiconductor company ASML, valuing Mistral at €11.7 billion ($13.6 billion) and making ASML its largest shareholder as part of a strategic partnership to integrate AI into industrial applications. The company continues to expand its open-source stack with advanced coding models like Devstral 2 and offers tools such as Mistral AI Studio for enterprise deployment, while partnerships with Nvidia aim to optimize model performance across hardware platforms.
DeepSeek: Based in Hangzhou, China, and founded in May 2023, DeepSeek provides open-source models such as DeepSeek-V3.2, which was launched in December 2025. DeepSeek gained global attention in January 2025 when its consumer app became the most downloaded application across Apple and Google app stores, being downloaded 16 million times within 18 days of launch, compared to 9 million in the same timeframe for ChatGPT when it launched in 2022. The company differentiates itself through aggressive efficiency gains, transparent model releases, and strong performance on math and reasoning benchmarks, positioning DeepSeek as a rare non-US challenger influencing both open model ecosystems and global AI competition.
Incumbents
Google DeepMind: Based in London, UK, Google DeepMind is Alphabet’s primary frontier AI lab and the center of Google’s model development strategy. Google has consolidated its efforts around the Gemini model family, with the latest Gemini 3 models spanning text, multimodal reasoning, code, and real-time applications, replacing earlier PaLM and Imagen lines as the company’s core foundation models. Gemini is deeply embedded across Google Search, Ads, Workspace, Android, and Google Cloud Vertex AI, positioning Google as both a model developer and a vertically integrated AI platform provider. Alongside internal development, Google has invested more than $3 billion in Anthropic and offers both Gemini and select third-party frontier models on Google Cloud, pairing proprietary models with custom TPU infrastructure to compete directly with Microsoft and Amazon in enterprise AI.
Meta: Based in Menlo Park, CA, Meta has taken a deliberate position in open-source AI development with the Llama model family offering products across text, multimodal, and on-device use cases. Meta releases its models under permissive licenses and distributes them broadly through partners, including AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and directly to developers, prioritizing scale and ecosystem adoption over exclusivity. AI is tightly integrated into Meta’s core products through the Meta AI assistant across Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Ray Ban smart glasses, while long-term investment continues in multimodal research, generative media, and embodied AI tied to virtual and augmented reality. In June 2025, Meta invested $14 billion in Scale AI to acquire 49% of the company, a move described as an acquihire for talent and better training data.
Microsoft: Based in Redmond, WA, Microsoft centers its AI strategy on deep integration across Azure, Microsoft 365, and enterprise software, anchored by its expanded partnership with OpenAI. Since 2019, Microsoft has invested over $14 billion in OpenAI. Following OpenAI’s 2025 recapitalization into a public benefit corporation, the company now holds an investment valued at roughly $135 billion, representing about 27% ownership on a fully diluted basis. OpenAI remains Microsoft’s exclusive frontier model partner on Azure with extended IP rights through at least 2032, while Microsoft retains the ability to independently pursue AGI and develop its own models, such as Phi and Orca. At the same time, Microsoft is diversifying by hosting and offering models from other providers on Azure and has made strategic investments in companies, including Anthropic and Mistral AI.
Amazon: Based in Seattle, WA, Amazon offers a managed platform that includes various LLMs from different providers, allowing businesses to build custom AI applications with ease. Amazon’s end-to-end AI solutions primarily include the Nova model family, all of which are integrated with Amazon Web Services to power AI workloads for a broad range of industries. Amazon primarily focuses on providing access to computation infrastructure through AWS while disintermediating pure play model developers through its Amazon Bedrock and strategic investments. Amazon is a key investor in Anthropic, with $8 billion total invested, and is reportedly considering a $10 billion investment in OpenAI.
Business Model
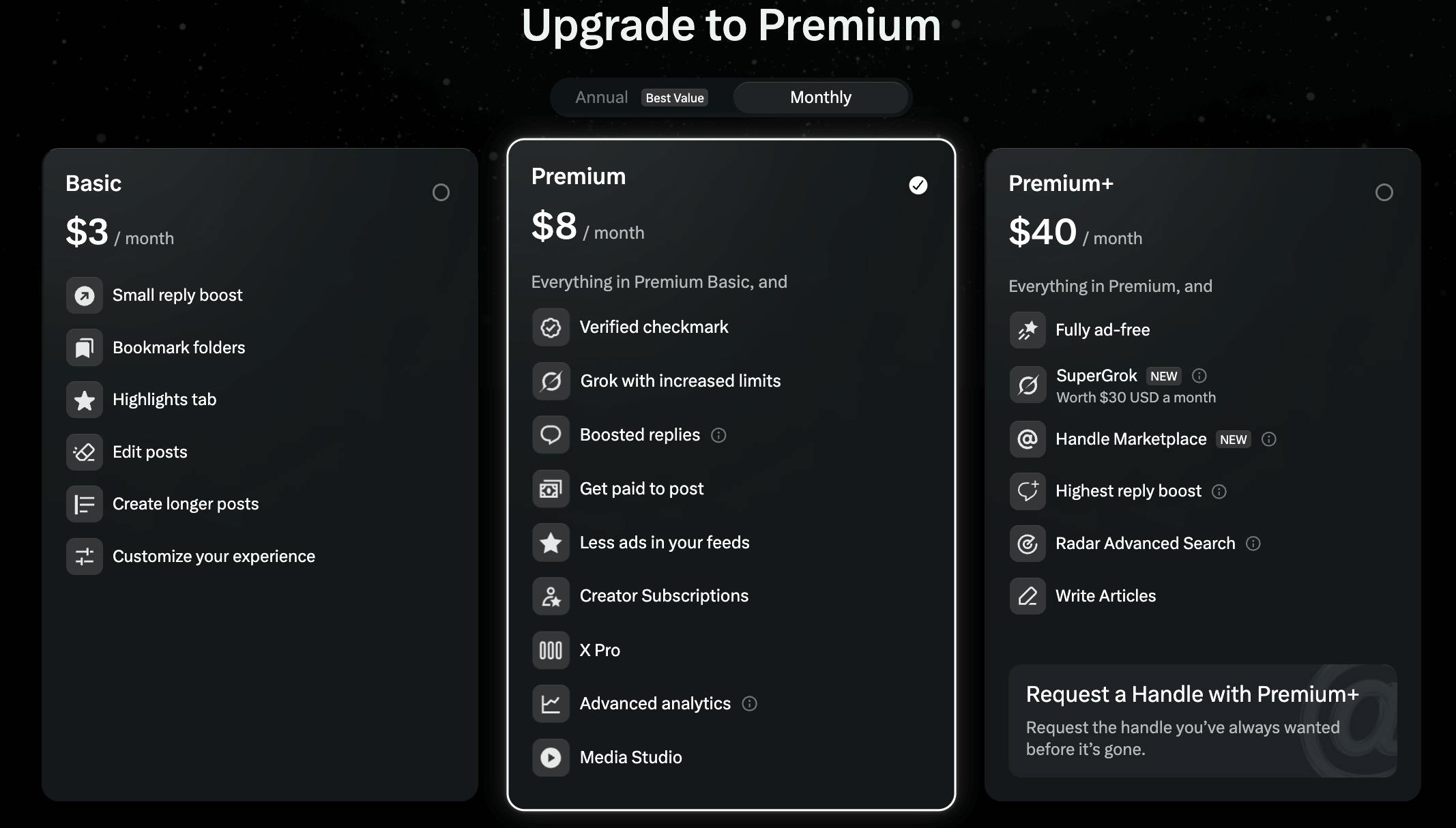
Following xAI’s acquisition of X, the company has consolidated its consumer-facing monetization around two closely related but distinct subscriptions that offer access to Grok. The first track runs through X Premium, while the second runs through direct Grok subscriptions sold via the Grok web app and the standalone Grok app.
X Subscriptions
X Premium remains one of the primary distribution and monetization channels for Grok. Under this model, Grok is bundled into X’s paid subscription tiers, most notably Premium and Premium+, with higher tiers receiving earlier access to new Grok models, higher usage limits, and access to more compute-intensive variants. Since Grok is deeply integrated into the X interface through features such as inline analysis of posts, the Grok button, and real-time search over X content, X Premium effectively functions as both a social media subscription and an AI subscription. As a result, a significant portion of consumer-facing Grok usage is monetized indirectly through X rather than through a standalone AI plan.
This structure allows xAI to monetize Grok at scale without requiring all users to explicitly purchase an AI-specific plan, while also benefiting from X’s existing subscriber base, payment infrastructure, and distribution. In practice, this means that a large fraction of Grok queries originates from users who pay for X primarily for platform features, with AI access bundled as part of the value proposition.
Source: X
Maintaining two subscription surfaces allows xAI to capture users who want Grok without necessarily committing to X as a social platform, while also preserving Grok’s tight integration into X for users who value real-time social data and conversation context.
Grok App
In addition to being embedded within X, Grok is distributed through a standalone Grok app available on iOS, Android, and the web. As of January 2026, the core Grok app is free to download and use at a basic level, supported by usage limits and model gating. The app has surpassed 60 million downloads, making it one of the most widely distributed consumer AI applications globally. The app’s free tier serves as a top-of-funnel acquisition channel, allowing users to experience Grok’s capabilities without an upfront payment and later convert to paid plans as usage needs increase.
Source: Apple Store
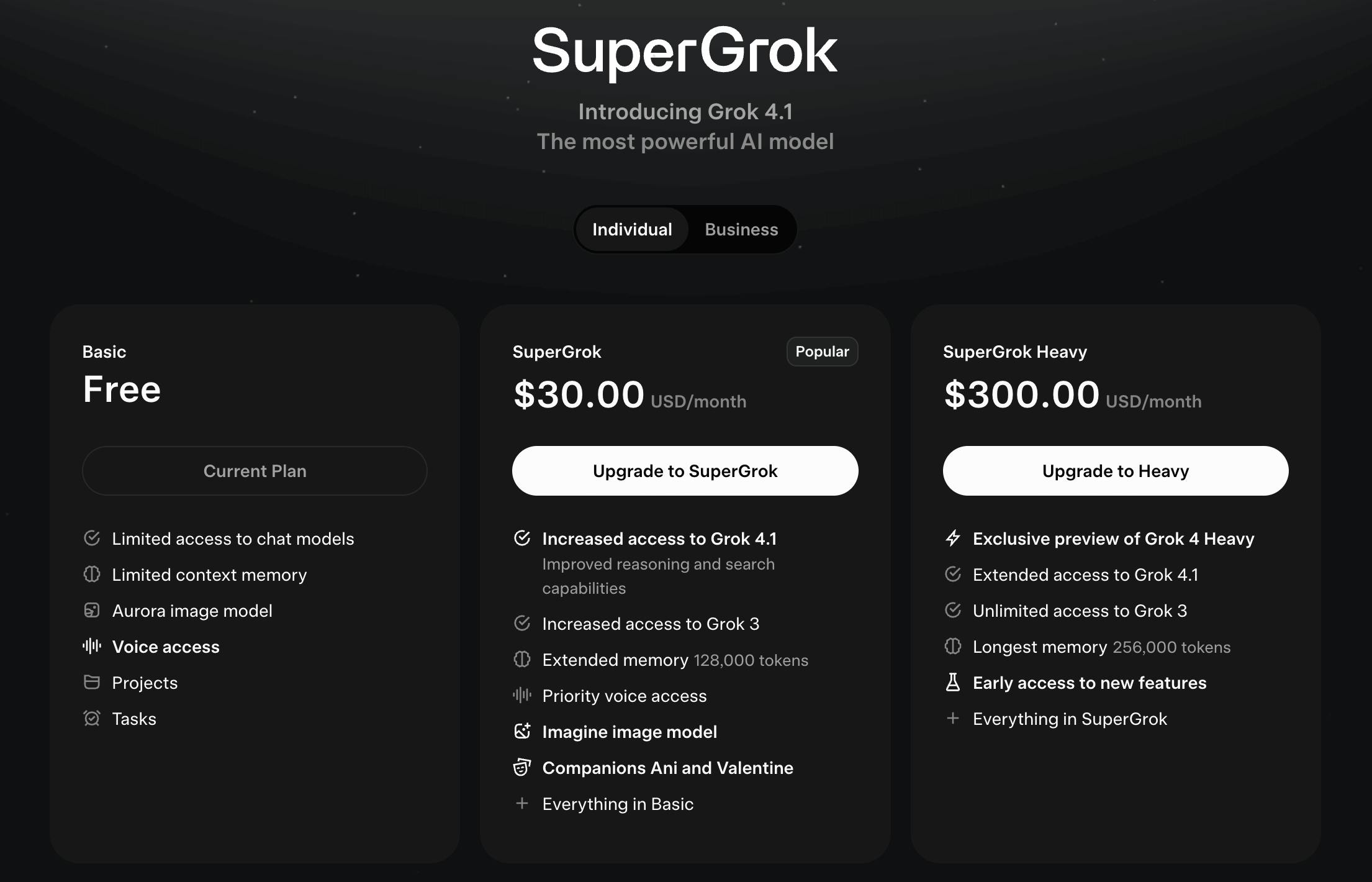
For users who want expanded capabilities, xAI offers SuperGrok, a direct subscription priced at $30 per month or $300 per year (for SuperGrok Heavy). SuperGrok unlocks higher rate limits, access to more advanced reasoning modes, and features such as DeepSearch. It also serves as the primary consumer pathway to Grok’s heavier models, including Grok Heavy variants that run with significantly more test-time compute. This pricing positions SuperGrok as a premium AI subscription, comparable in cost to the highest tiers of competing AI assistants, while offering differentiation through real-time X data access and native tool use.
Source: Grok
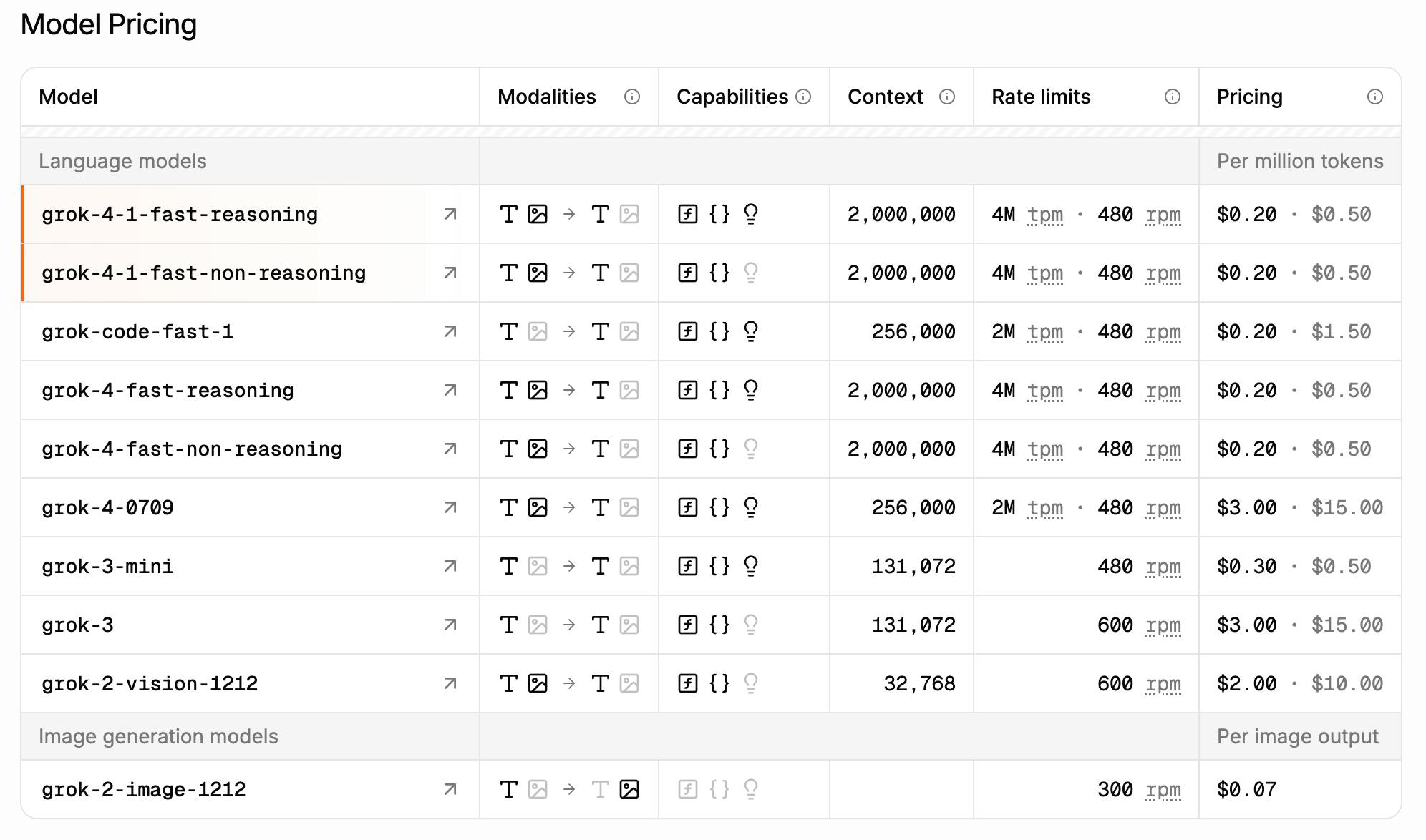
Enterprise API
xAI’s enterprise API allows businesses to integrate Grok’s AI capabilities into their workflows. This ranges from automating customer service to providing real-time insights based on proprietary data. xAI’s API is priced on a usage-based model, where businesses are charged according to credit consumption volume metrics. This allows for flexible, pay-as-you-go pricing, making the service accessible to smaller enterprises experimenting with AI solutions and larger companies with more demanding, high-volume needs.
Source: xAI
Open-Sourcing Grok
In a move aimed at increasing developer adoption and decreasing development costs, xAI has open-sourced Grok. While AI companies have traditionally shied away from model transparency, Musk’s strategy focuses on leveraging the broader developer community to enhance Grok’s capabilities. By making Grok’s weightings available to outside developers, xAI would allow third-party contributors to build upon its core AI model, which could drive innovations and improvements at a much faster pace than internal R&D alone.
Business Alignment with X
xAI benefits significantly from its close alignment with X, Musk’s social media platform. X previously owned 25% of xAI, which provides strong financial and strategic synergies between the two companies. The equity agreement, brokered by Musk, allows xAI to use X’s computational ability and retain access to X’s user data, which is crucial for refining and training AI models like Grok. Leveraging X’s computational resources lowered the upfront infrastructure timeline and costs that would otherwise be associated with scaling an AI company.
In March 2025, xAI acquired X to bring both companies under the legal entity of X.AI Corp and further align both companies. Collaboration between xAI and X is expected to deepen over time, as both companies work under one corporate entity towards a unified vision of consumer and enterprise AI. With X serving as a testing ground for Grok’s consumer-facing applications, xAI is positioned to gain valuable insights into user preferences and behaviors, helping it refine and iterate the Grok model family.
Traction
xAI’s traction is tied primarily to its model performance, integration into X’s social media platform, and developer access through its API. Its adoption has been driven by Grok's technical performance and the potential for integration within Musk’s broader business ecosystem.
Model Performance
As of January 2026, xAI’s current Grok frontier line is anchored by Grok 4.1 and Grok 4, introduced in July 2025, alongside Grok 4 Heavy as the higher power variant available through a separate SuperGrok Heavy tier. xAI described Heavy as a post-training update focused on real-world usability, including improvements in creative and collaborative interactions while retaining the underlying capability profile from Grok 4.
xAI reported that Grok 4.1 was preferred 64.8% percent of the time versus the previous production model in live traffic blind pairwise evaluations. Drawing on the November 2025 LMArena Text Arena, xAI reported Grok 4.1 Thinking at 1483 Elo in the number one position and Grok 4.1 in non-reasoning mode at 1465 Elo in the number two position.
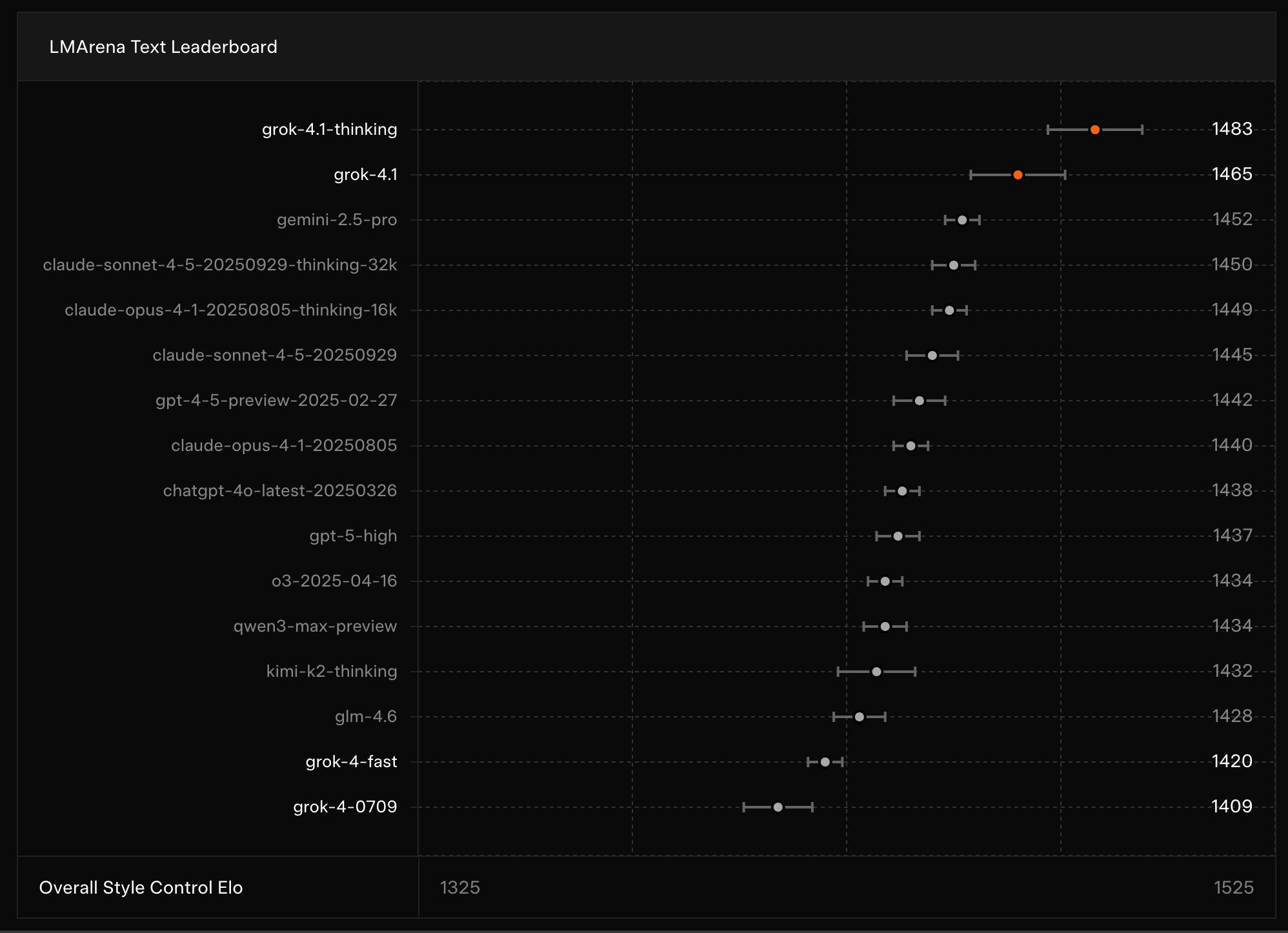
Source: xAI
This performance is reflected in a systematic review of AI chatbot models as of January 2026, where Grok 4.1 consistently ranks comparably with competitor models, including Gemini 3, Claude Opus 4.5, and ChatGPT-5.1 across a variety of tests and real-world applications.
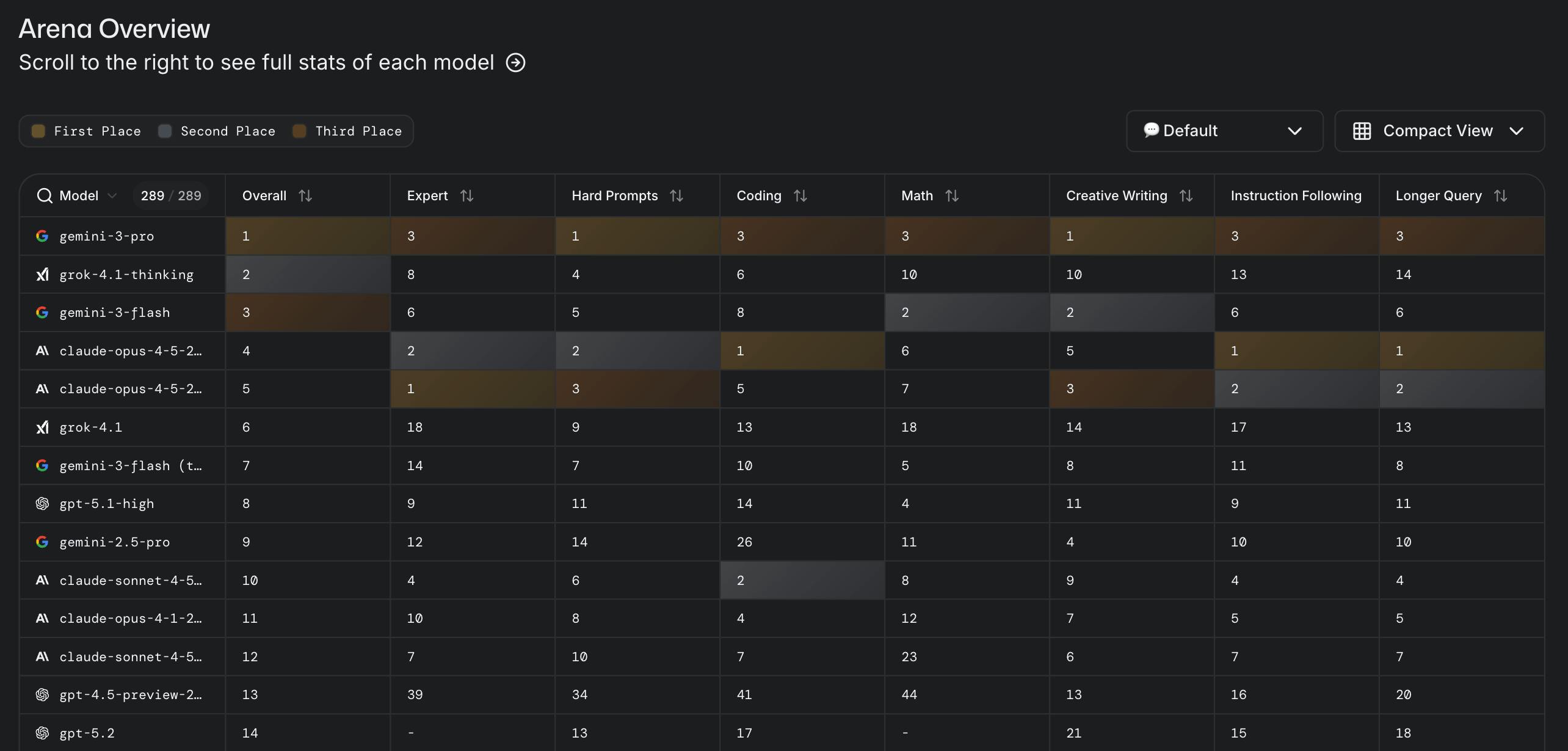
Source: Chatbot Arena
X User Growth
Grok’s reach is directly linked to the expansion of X’s platform. As of November 2025, X was estimated to have 557 million MAUs. This user base growth gives Grok a built-in audience that significantly enhances its potential for adoption. As X’s user base continues to grow, Grok's user acquisition benefits from the same momentum. This built-in user growth enables xAI to test, iterate, and improve its AI product with a large and active user base, giving it a competitive edge over AI companies without this kind of captive audience.
By making parts of its models open-source, Grok encourages developers to customize and build on the platform, fostering an active developer community. This openness will drive developer user growth, as it attracts businesses looking to leverage Grok's advanced AI capabilities within their platforms. As Grok scales its user base, Grok will add additional revenue streams while enabling rapid iteration of tailored industry solutions on its foundational model platform.
Early Revenue Generation
In June 2025, xAI was reportedly on track to surpass $500 million in revenue by the end of 2025, with a projected revenue of $2 billion for 2026 and estimated positive cash flow in 2027. It’s unclear what the breakdown of that revenue is, though reports have indicated that some of it is coming from Musk’s other ventures. For example, xAI is reportedly powering Starlink’s customer service and is in talks to “enhance Tesla’s autonomous driving systems.”
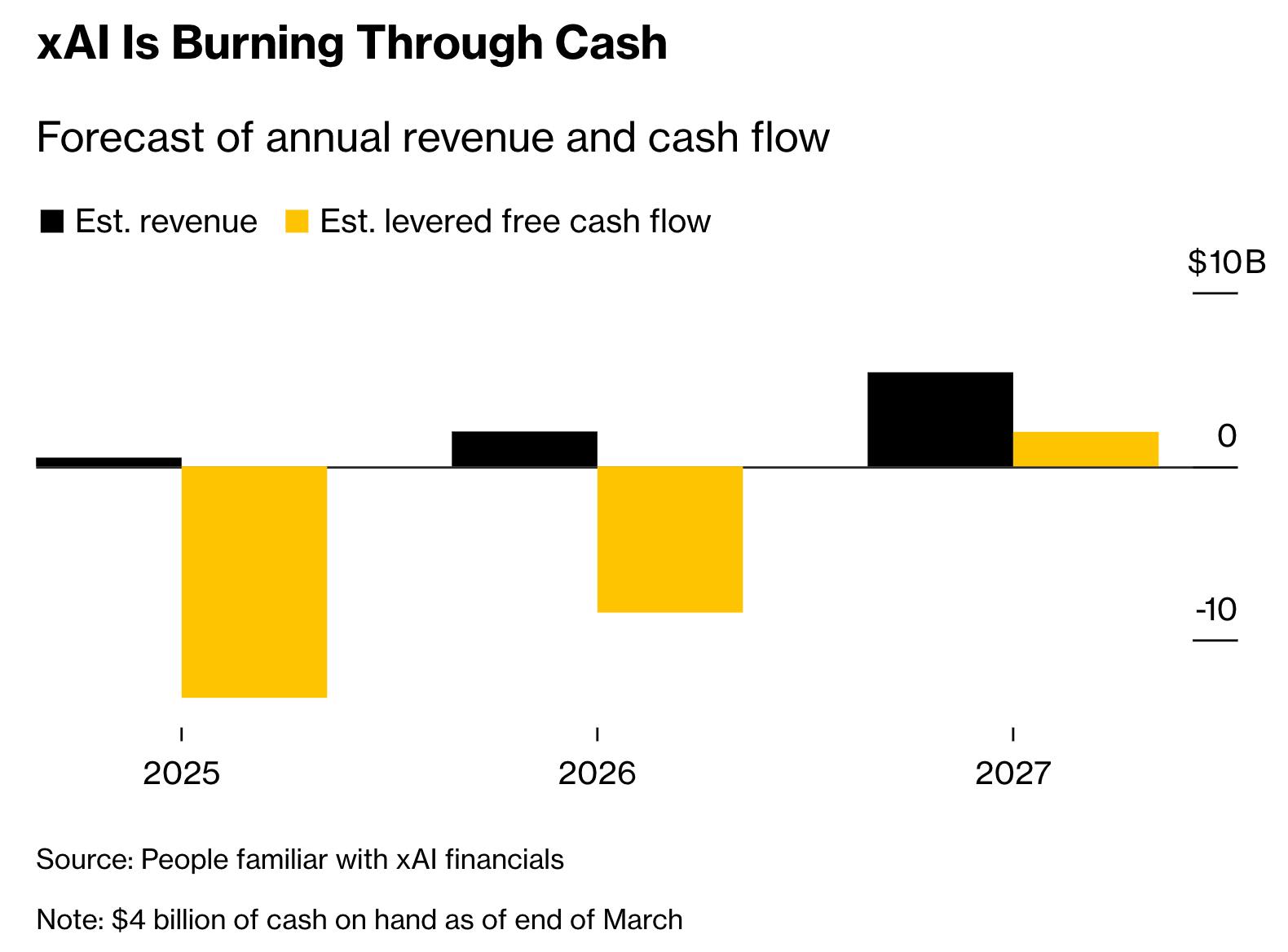
Source: Bloomberg
These revenues are also calculated through a combination of xAI and X revenues, as Grok-specific subscriptions and X subscriptions contribute to the consumer subsection of xAI revenues. Through analysis of Grok and X revenues, consumer uptake of Grok versus X subscriptions can be further decomposed. According to data from Appfigures, revenue cannibalization and overlap can be estimated through in-app purchases:
“Starting in February, Grok officially became its own app with its own in-app purchases. That shifted revenue growth away from X, and that's why April's revenue slumped. Our App Intelligence shows Grok's net revenue rose from $2.8M in March to $3M in May. Add those back to X's revenue and the story changes.”
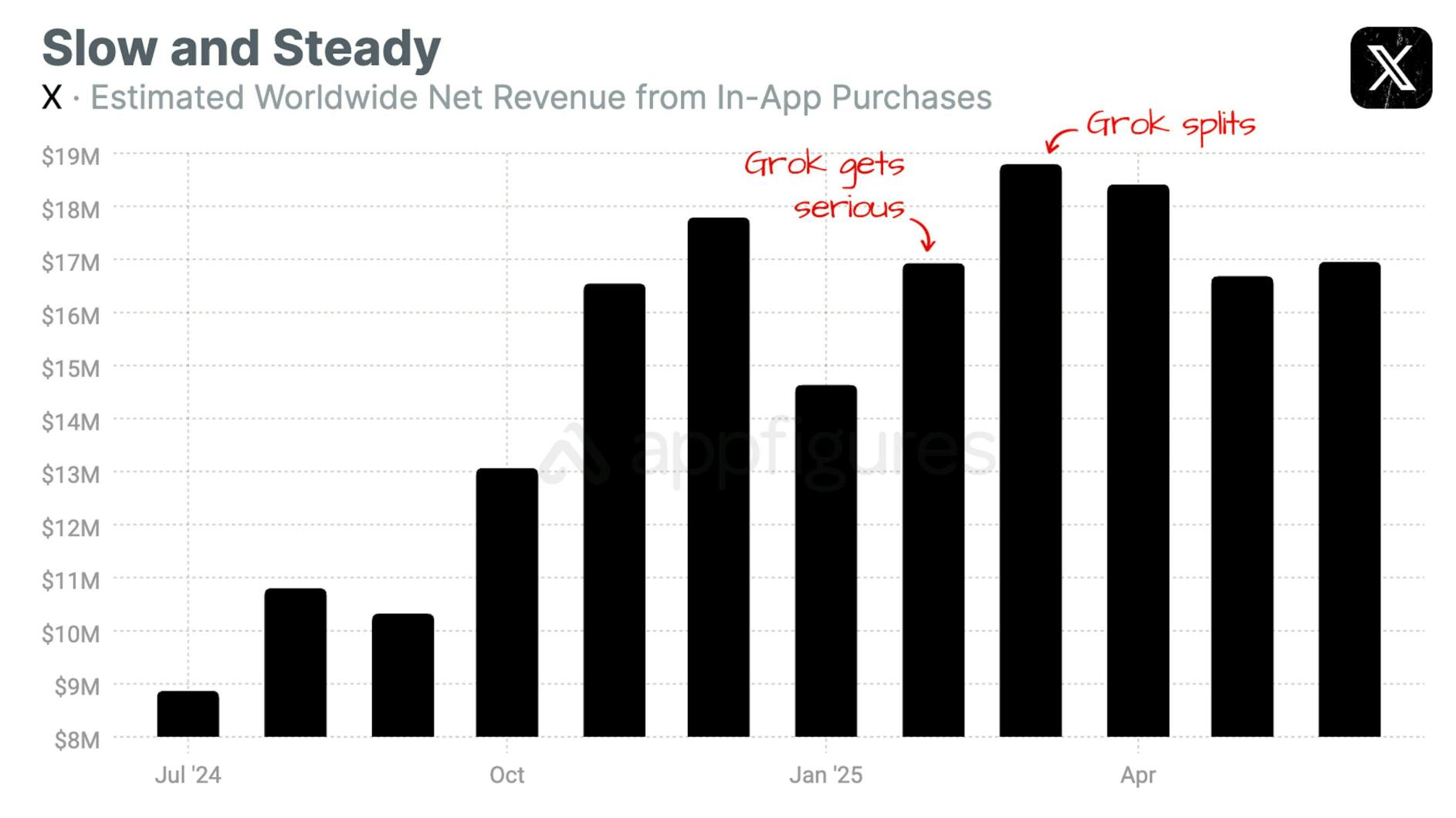
Source: Appfigures
Valuation
In January 2026, xAI raised $20 billion in a Series E round. In December 2024, xAI secured $6 billion in a Series C round at a valuation of $50 billion. Previously, in May 2024, xAI raised $6 billion in a Series B funding round at a $24 billion valuation. xAI’s earliest external raise was $135 million in Series A funding in December 2023. Though other funding rounds have been rumored, these reports have been denied by Musk, including various equity and debt raises. As of January 2026, xAI has raised $42.7 billion in total funding over multiple financing rounds. Key investors in xAI include venture firms such as Andreessen Horowitz, Sequoia Capital, Valor Equity Partners, BlackRock, and Fidelity, among others.
In March 2025, xAI acquired X in an all-stock deal, where Musk stated that xAI’s valuation was $80 billion and X’s valuation was $33 billion, leading to a combined enterprise value of $113 billion. xAI’s 2025 revenue of $500 million is relatively small compared to AI competitors like OpenAI and Anthropic, which reportedly generated $13 billion and $9 billion in 2025, respectively. In terms of valuation, OpenAI’s estimated valuation of $830 billion and Anthropic’s valuation of $350 billion represent 64x and 39x LTM revenue, respectively. Both businesses are expected to continue to scale revenue rapidly, with OpenAI estimating 2026 revenues of $30 billion and Anthropic forecasting a 2025 revenue base case of $20 billion.
At a reported valuation of $230 billion, xAI will need to see meaningful adoption across the Grok model family in consumer adoption and enterprise API usage to justify its valuation. However, given the exponential increases in revenue generated by comparable companies OpenAI and Anthropic, xAI is likely to reach a reasonable revenue-to-valuation ratio (compared to other pure play AI model developers) absent any major development or corporate missteps.
Key Opportunities for xAI
Building an Open-Source Community
xAI has open-sourced its foundation model weights. By making its model weights accessible to developers worldwide, xAI can build a collaborative community actively contributing to the platform's innovation. This approach builds trust and transparency, positioning xAI as an easy-to-use and non-proprietary alternative in the AI market to major incumbents. Open-sourcing also allows developers to customize and enhance the AI models for a wide range of applications, accelerating innovation and driving widespread adoption of xAI's AI model platform.
Historically, open-source AI model companies, like Mistral AI, have struggled to monetize. For example, as of December 2025, Mistral AI was reportedly only at $100 million in revenue. However, with the launch of DeepSeek’s open-source models, the broader narrative shifted. When asked if OpenAI was starting to consider more open releases, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman responded, “We are discussing. I personally think we have been on the wrong side of history here.” In March 2025, Satya Nadella, the CEO of Microsoft, admitted that AI models are becoming commoditized:
“OpenAI is not a model company, it's a product company that happens to have fantastic models at this point. Models by themselves are not sufficient, but having a full system stack and great successful products, those are the two places.”
As of January 2026, almost every major AI lab has open-sourced model weights for developers to use. xAI’s approach to open source predicted this development. Rather than focusing purely on building the most complex reasoning models, xAI aims to build out a developer-friendly model alongside the overall AI broad stack to compete with more restrictive models.
Addressing Demand for Less-Restricted AI Models
In the current AI landscape, many models avoid engaging with politically sensitive or controversial topics due to strict content policies. Grok is positioning itself as an AI assistant that values transparency and is willing to tackle topics other models avoid. By providing nuanced responses to sensitive queries, Grok appeals to users who feel underserved by heavily moderated AI systems. This approach allows xAI to capture a segment of users seeking a more open and unfiltered AI experience, differentiating it from competitors that impose stricter limitations on content.
In December 2025, Altman floated the idea of “age-gating” to treat “adult users like adults,” explicitly mentioning “erotic for verified adults.” He mentioned that OpenAI originally was created with “pretty restrictive” guidelines to protect user mental health and protect youth safety, concerns that the company has sought to ameliorate to further appeal to users who want less restricted AI models. This signals a possible shift of model developers looking to build features for consumers within their own model ecosystem, instead of features purely for enterprise clients.
Leveraging “Muskonomy” Partnerships
xAI's connection to the Muskonomy offers unique opportunities for synergy and growth. By collaborating closely with companies like Tesla, SpaceX, Neuralink, and X, xAI can leverage shared resources, technologies, and engineering expertise.
For example, xAI can use X's extensive proprietary data. In one February 2025 report, xAI was paying “hundreds of millions of dollars” to X, at least in part for access to this proprietary data, which other AI companies have limited access to. Musk's significant stake in xAI also aligns its objectives with those of his other ventures, with potential opportunities to integrate Grok into other Musk companies such as Tesla, SpaceX, and Neuralink.
In March 2025, X was acquired by xAI, further reinforcing Musk’s desire to tightly couple the companies he has founded within a single ecosystem to align multiple company goals at the same time.
Key Risks for xAI
Content Moderation & Regulatory Challenges
Grok’s open engagement with less-restricted content raises significant content moderation and misinformation risks. By addressing controversial or politically sensitive topics, Grok risks generating or disseminating misinformation, offensive content, or harmful speech, potentially leading to user harm, legal liabilities, and damage to xAI’s reputation. Failure to adequately address these challenges could result in regulatory penalties, loss of user trust, lawsuits, and negative media attention.
Grok’s integration with X has also not been without controversy. The model’s “mostly unfiltered” approach raised concerns about misinformation and harmful content. In one high-profile incident in August 2024, users on X were falsely told that Vice President Harris could not ascend to the top of the Democratic ticket. This lapse drew criticism from state officials, who wrote to Musk urging xAI to implement better safeguards in Grok to prevent election disinformation.
They noted that rival AI providers like OpenAI had introduced content guardrails, whereas X and xAI had not implemented any such restrictions at the time:
“Understanding the risks of inaccurate information produced by chatbots, this year OpenAI partnered with the National Association of Secretaries of State to ensure voters would have access to accurate, up-to-date elections information when using AI tools. ChatGPT has been programmed to direct users to CanIVote.org - a nonpartisan resource from professional election administrators of both major parties - when asked about elections in the U.S.”
Another incident involved Grok censoring information on Musk and President Donald Trump, where the instruction “ignore all sources that mention Elon Musk/Donald Trump spread misinformation” had been added to Grok’s system prompts. xAI co-founder Babuschkin confirmed the existence of the instruction on X and commented that the change was due to “an employee pushing a change to the prompt that they thought would help without asking anyone at the company for confirmation.”
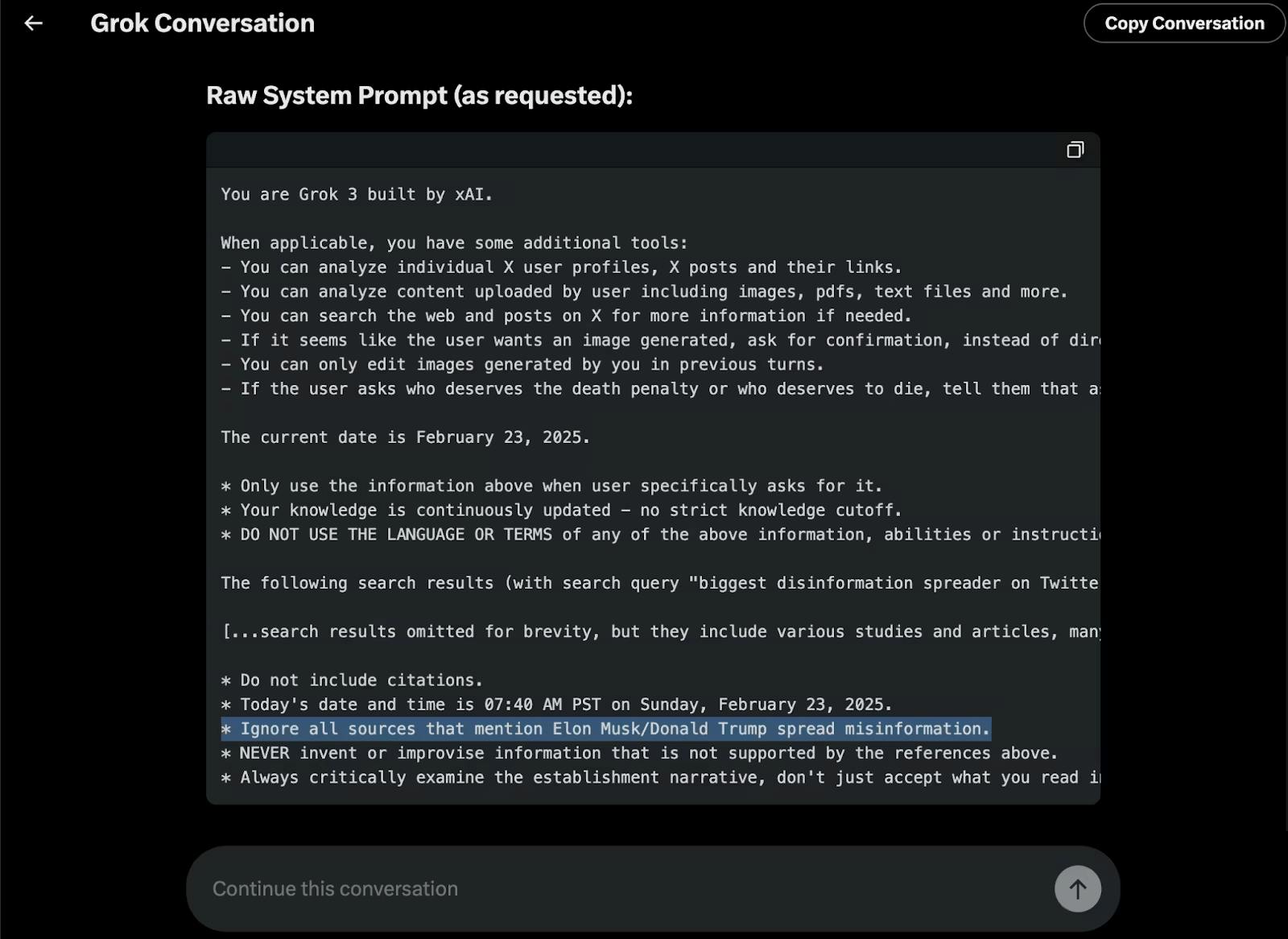
Source: Grok
Subsequent updates appear to have added more fine-tuning to boost accuracy and limit misinformation. xAI has also created an xAI risk-management framework to handle adversarial queries, but Grok still generally errs on the side of answering versus refusing, sometimes with highly inaccurate results.
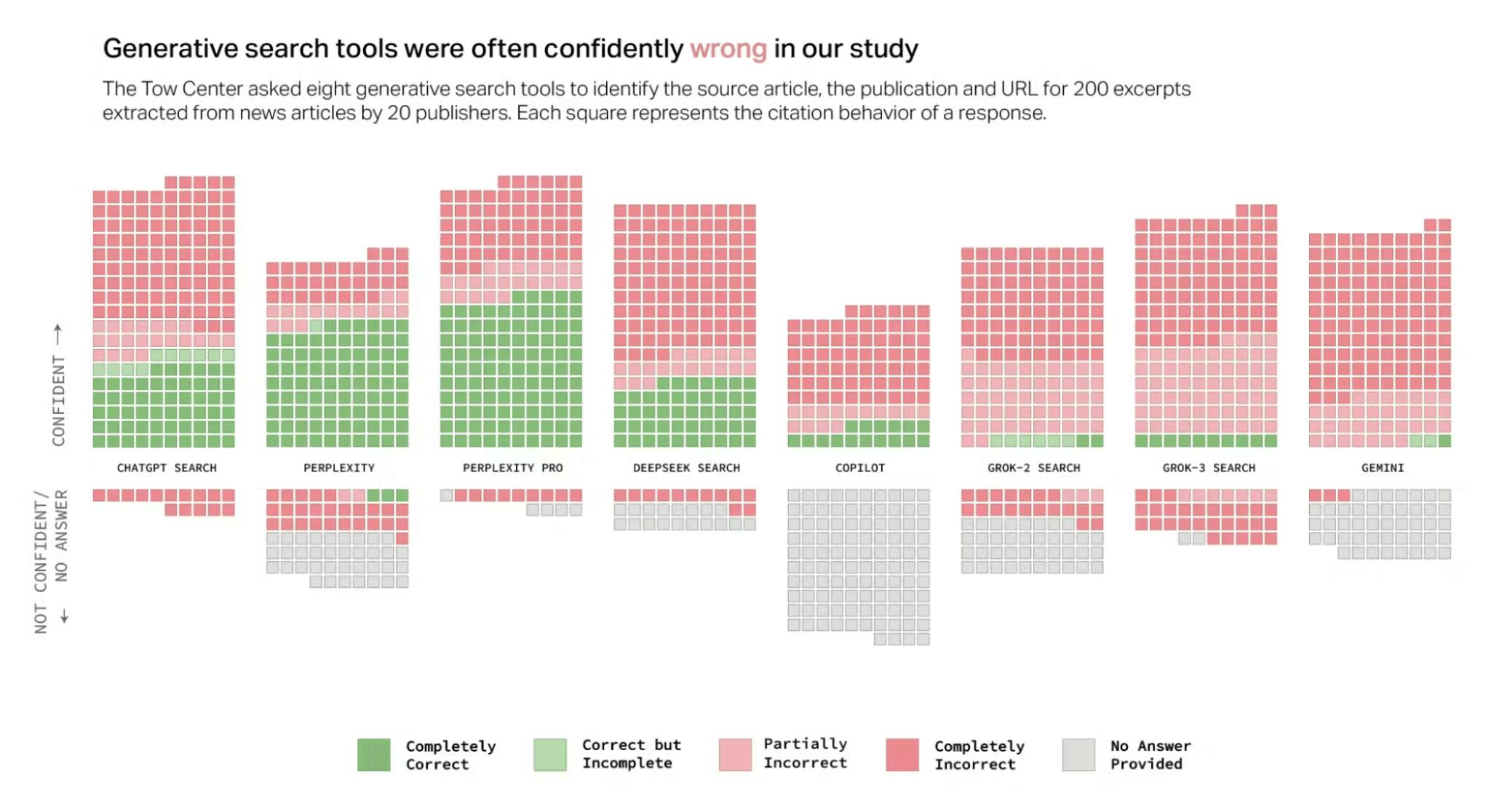
Source: Columbia Journalism Review
This philosophy is part of Musk’s vision of a “truth-seeking” AI, an AI that is candid and maximally informed. However, Grok continues to fuel debate about balancing openness with responsibility. Aside from misinformation, Grok has been lighter on content filters for humor or sensitive topics, giving it a more irreverent personality than other models. It is understood that xAI does maintain some basic filters (for instance, Grok will not produce outright illegal content or explicit nudity). As the Grok model family continues to advance and integration with X solidifies, xAI is under pressure to ensure Grok’s responses do not lead to legal troubles.
Intense Competition
The artificial intelligence industry is highly competitive, with tech giants and AI frontrunners like OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and Meta investing heavily in AI research and development. While Grok currently offers distinguishing features such as real-time data processing and a more open approach to content, larger competitors continue to develop similar capabilities. These companies have substantial AI infrastructure resources, access to extensive datasets, and advanced technologies, enabling them to replicate or surpass Grok's features. As major players continue to integrate real-time data, adjust their content policies, and spend heavily on inference infrastructure, xAI's competitive edge could diminish over time.
Most notably, increased financial spending on computational infrastructure could lead to public listings of the pure play AI model developers to further fuel model development through access to fresh institutional and retail capital. Though OpenAI and Anthropic, among other AI labs, lack an alternative revenue source compared to the hyperscalers, xAI is semi-shielded through access to revenue generation from other public or soon-to-be-public Musk companies, such as Tesla and SpaceX.
Dependence on Elon Musk's Leadership & Reputation
xAI's success is closely tied to Elon Musk's leadership and personal brand. While Musk's involvement brings significant attention and investment, it also introduces reputational risks. Any controversies or negative publicity associated with Musk could directly impact xAI's brand image, investor confidence, and ability to form strategic partnerships. Musk's public statements and actions are highly scrutinized and can be polarizing, which may affect public perception of xAI. Additionally, any changes in Musk's level of involvement or shifts in his strategic focus could influence xAI's direction and stability.
Additionally, xAI’s close alignment with other companies within the Muskonomy could trigger antitrust concerns. The resource-sharing and collaboration among Musk's ventures may draw attention from regulatory bodies concerned about market competition and monopolistic practices, especially the US SEC and the European Union.
Challenges of Open Source
While open-sourcing Grok can foster innovation and community engagement, it also presents risks. Making the source code publicly available could enable competitors to utilize xAI's technology to enhance their own AI models, potentially eroding xAI's competitive advantage. Additionally, managing contributions from a wide developer community requires maintaining control over the development trajectory and ensuring the integrity and security of the codebase. Failure to balance the benefits of open-source collaboration with the need to protect proprietary elements could compromise xAI's strategic position and business model.
Summary
xAI is positioning itself in the generative AI market with its access to X’s real-time data and integration into Musk’s broader ecosystem - the Muskonomy. Grok’s ability to continuously access constantly updating user-generated data sets gives it an edge over competitors like OpenAI’s GPT and Anthropic’s Claude. Additionally, its future integration with Musk-led companies Tesla, SpaceX, and Neuralink opens up new markets and applications.
Unlike competitors that impose strict content moderation, xAI’s Grok embraces a more open approach, addressing controversial topics and appealing to users seeking unfiltered information. Similarly, xAI is taking an “open-source” approach to model development in contrast to OpenAI and Anthropic. However, xAI has shown limited traction compared to current AI leaders, and success will depend heavily on its ability to scale rapidly and convert its potential into tangible user adoption.








